When a person needs to quickly make an accurate diagnosis and check whether there are any pathologies of internal organs, the magnetic resonance imaging method is used.
This technology is based on the use of an intense magnetic field.
In this case, the patient is placed in a special tomograph, and doctors receive a cross-sectional view of various organs.
In this article we will look at the potential health risks of MRI. This will allow you to understand whether the examination can be carried out in a particular case.
Experienced radiologists study the compiled 3D model and find potential changes at a very early stage.
Which tomograph should I choose for MRI of the spine?
It becomes more and more difficult to make a mistake when choosing an MRI Center in Moscow every year. For the most part, diagnostic centers are already equipped with modern high-field closed (tunnel) tomographs with a field strength of 1.5 Tesla.
PHOTO: Magnetic resonance imaging at MIBS Centers in Moscow is performed on high-field Siemens tomographs
Such devices combine high resolution images, suitable for identifying possible pathologies and injuries of the spine, with the optimal cost of MRI examination. Accordingly, the price of MRI diagnostics is optimal.
But there are also several “traps”. Despite progress, low-field tomographs (magnetic field strength less than 1.5 Tesla), both open and closed, are still represented on the capital market. And, in relation to MRI of the spine, they remain the lot of aggregator companies offering the lowest prices for MRI examinations in Moscow.
Illustration: Low-field tomography can be useful for visualizing large structures, but MRI of the spine using such a machine does not provide sufficient information
The resolution of MRI images of the spine using such equipment is usually insufficient to make an informed medical decision, and instead of saving, patients often have to pay more by undergoing repeated examinations at other MRI centers. But thanks to massive advertising and attractive prices (more precisely, declared impressive discounts - up to 40-60% of the average market cost of a high-quality examination), aggregator companies still receive a significant number of requests from patients. Moreover, MRI of the spine will only be possible for the first time under compulsory medical insurance.
Formatting QUOTE: Be careful not to pay twice!
As for the capabilities of ultra-high-field tomographs (3 Tesla and higher), world practice in the treatment of spinal diseases has shown the redundancy of this parameter. Accordingly, for the treatment of most pathologies and injuries, MRI of the spine performed on 1.5 Tesla tomographs is sufficient, and more expensive studies on an ultra-high-field tomograph are extremely rarely indicated.
Indications for tomography with contrast
Today, 1/5 of MRIs are performed using contrast. The decision to perform an MRI with or without contrast is made by the doctor. This method is preferable in the following cases:
- malignant neoplasms;
- suspicion of the presence of infection and inflammatory process in the body;
- multiple sclerosis;
- meningeal pathologies;
- problems with the spine;
- abnormalities of the digestive system;
- as a continuation of the study conducted without the use of a dye.
Preparing for the study
There are no fundamental differences in tomography with contrast compared to conventional one. But there are a few general recommendations before doing it:
- Before the examination, it is necessary to remove all objects made of metal. Mobile phones cannot be brought into a room with a magnetic installation.
- You should not use cosmetics, as metal microparticles can worsen the test result. The doctor should also be aware of the tattoos on the patient’s body.
- Dentures can also be removed.
Additional preparation will be required when examining abdominal organs - you will have to refuse food and water 5 hours before the scan. An hour before the examination of the pelvic organs, you need to drink 1 liter of water for greater reliability of the results. After preliminary images obtained without dye, an injection is performed, for which the laboratory assistant injects a contrast agent intravenously. After an MRI with contrast, the doctor compares the results of the studies to obtain maximum information about the condition of a specific area and make the correct diagnosis. And this is the first step on the path to recovery.
What determines the cost of an MRI of the spine?
Definitely, the price of MRI of the spine on a low-field tomograph is lower due to differences in technology, which explains the higher acquisition cost and maintenance cost of high-field tomographs (from 1.5 Tesla). But such savings are savings on the accuracy of the survey. In addition, an MRI of the spine on a low-field tomograph lasts about half an hour, which is twice as long as a tomography of the same volume on a high-quality 1.5 Tesla tomograph. Accordingly, the risk of patient movements causing blur in some images is twice as high.
With comparable technological support and qualifications of specialists (for example, MIBS radiologists who prepare reports for images regularly undergo full-time and distance learning and advanced training, including specific studies and features of “narrow” pathologies, such as identifying neurological pathologies or tumors), there are differences The cost of MRI of the spine may be determined by the following factors:
- scope of the survey (number of departments studied);
- justified need for administering a contrast agent (to identify inflammatory processes and tumors of the spine)
Saving on the administration of a contrast agent or the number of spine sections studied is the most “slippery issue” in the practice of MRI centers in Moscow. In particular, focusing on the rich experience and constantly improving system in the network of MIBS diagnostic centers for the quality of examinations, a significant part of patients choose us to undergo magnetic resonance imaging under compulsory medical insurance. However, insurance only covers MRIs of the spine without contrast within one anatomical area (compartment). But, for example, a suspicion of a tumor located at the border of two parts of the spine requires an MRI of two zones with contrast.
Illustration: Visual difference in the information content of MRI of the spine without contrast (left) and with contrast (right). The introduction of a contrast agent made it possible to determine the presence of XXX and promptly begin treatment
Regardless of the patient’s choice, doctors at MIBS centers in Moscow will provide the most informative conclusion available in the selected examination mode.
MRI or x-ray examination
Let's figure out what these definitions mean and what features these two types of diagnostics have.
Magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) is a method of obtaining layer-by-layer images of internal organs and tissues. The technique is based on the use of a magnetic field. The tomograph generates a constant magnetic field. Thanks to a special combination of waves, atomic nuclei are excited in the human body. Their response is measured by the machine, and an image of the internal structures is obtained.
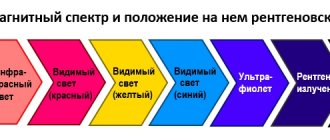
Radiography (or x-ray) is a method of obtaining a projection of the internal structure of organs using x-rays. They pass through the human body with varying degrees of attenuation, depending on the density of the tissue being examined, and are projected onto paper or film. This way a black and white photograph is obtained. The lighter the image on it, the denser the fabric.
Now let’s move on to assessing which is better, X-ray or MRI, consider the pros and cons of the methods and how they work.
Difference between MRI and X-ray
The differences between these methods are significant both in price and in the complexity of the equipment. Both examinations should show the projection of the internal organs on paper. In the case of X-rays, the same rays are used; dense tissues do not let them through, while soft tissues let them through with a slight change. Thus, on paper we see bones painted white, but internal organs, such as the lungs, appear dark. This method perfectly shows a fracture - quickly, simply and cheaply.
MRI is more complex both in hardware and in understanding. The principle of operation is based on the fact that there are many hydrogen atoms in the human body, which respond when in powerful magnetic fields, and by how many there are, a picture is obtained: the lighter, the more atoms. For example, there is a lot of hydrogen in the brain, and it will appear almost white. MRI is more accurate than x-rays, and it is easier for the doctor to find the cause of the patient’s complaints.
Limitations for MRI and X-rays
All diagnostic methods have contraindications. Thus, the restrictions for undergoing MRI are:
- ferromagnetic metal in the body (pacemaker, middle ear implant, metal implants, Ilizarov apparatus, hemostatic clips, tattoo ink with metallic inclusions, dentures);
- claustrophobia;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- kidney disease (during examination with contrast).
If you have no contraindications, then MRI is completely safe for you. Despite the large dimensions and noise, the harm from the device is the same as if you hold a magnet.
X-ray limitations include pregnancy, childhood (before puberty), and open pneumothorax. When using contrast, contraindications include: diabetes mellitus (in the stage of decompensation), pathologies of the liver, thyroid gland, kidneys, open type of tuberculosis. It is also not recommended to do this procedure too often. In addition, a general contraindication for both methods when using contrast is an allergic reaction in the patient to the components of the contrast drug. If radiography is performed infrequently, under the supervision of a physician and with the radiation dose recorded in the patient’s outpatient record, then the harm from ionizing radiation is almost eliminated. In this case, it cannot be said which is more harmful, X-ray or MRI. Both methods are quite safe. Especially if radiography is carried out in a well-equipped clinic using a modern device.
When is MRI used and when is X-ray used?
These methods complement each other, and radiography is often used first. If it turns out to be insufficient, then they are sent for an MRI. For example, you have back pain, perhaps something wrong with your spine, and you are sent for an x-ray. If nothing is found, then you will be referred for an MRI, which may show, for example, a problem with the intervertebral disc. Another example. Your knee joint hurts. An X-ray shows that your knee is intact, but an MRI shows a torn meniscus. And one last example. You have severe pain in your arm, the doctor sends you for an x-ray, and it shows a fracture. Then additional diagnostics are not needed. However, only MRI is used to analyze the brain, as well as computed tomography (CT).
Dangers of MRI and X-rays
Danger during procedures exists only with radiography, because the patient is irradiated. This is not the case with MRI. Therefore, the answer to the question of which is safer, MRI or X-ray, is, of course, MRI.
Contraindications to MRI with contrast
Negative effects of the dye during the study were excluded. It does not lead to complications after the procedure. There are few contraindications, these are:
- the first 3 months of pregnancy due to the special susceptibility of the fetus;
- individual intolerance to any component of the coloring matter;
- bronchial asthma;
- renal and liver failure. Nephrogenic fibrosis may result from the use of gadolinium;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- dehydration of body tissues;
- taking certain medications, for example, β-blockers.
In all other cases, including children, tomography with contrast can be performed. Sometimes circumstances force even an expectant mother to undergo an MRI using dye. Contrast agents are excreted in feces and do not have any side effects on the health of the subject. Factors unfavorable for the study cannot be considered as definitive. The decision on admission is made by the doctor treating the relevant pathology.
Which doctors will need MRI images of the spine?
Considering the impact of the condition of the spine on the functioning of the entire body, MRI examinations are prescribed by doctors of different specialties: a neurologist, neurosurgeon, oncologist, cardiologist, rehabilitation specialist and even a therapist in many cases will rely on data from magnetic resonance imaging of the spine. Are you worried about headaches, dizziness, limbs that “don’t obey” or go numb, or the functioning of the heart and other internal organs is disrupted? Perhaps MRI of the spine will provide an answer about the cause of the disorders and possible directions for their elimination.