Optical coherence tomography of the eye has become widespread in clinical ophthalmology over the past 15 years. The popularity of this innovative technology is easily explained by the ability to visualize intravital structures of the eyeball in high quality and resolution. Of course, during the existence of this research method, technology has made significant strides forward. The article is an overview of the principles of operation of modern equipment for optical coherence tomography, as well as the most significant clinical aspects of this examination technique, indications for its implementation and the cost of optical coherence tomography on the Moscow medical services market.
What is CT eye
Computed tomography of the eyes is a highly informative and most popular method for studying all components of the visual system. Recently, a large number of doctors specializing in ophthalmic diseases have resorted to using the presented scanning method. Typically, such an examination is prescribed to patients to identify bone abnormalities and formations of a benign and malignant nature. According to average statistical indicators, almost every year on the planet the progression of metastases in the orbital region increases in patients. Computed tomography helps to cope with such problems quite effectively, since with its help it is possible to study and find oncology at the initial stage of its development.
The operating principle of such a clinical device is to produce x-ray radiation that passes through a specific area (in our case, the head area). Subsequently, the information obtained is transformed on the monitor into a clear and detailed image in the form of several projections. During the CT eye procedure, specialists obtain results with characteristics of the structure of the nerve, arteries and veins of the retina, lacrimal systems, eyeball and muscles. When performing a CT scan of the eye orbits, an ophthalmologist can identify various sources of inflammation, degeneration, growth of formation or injury.
Using the simple and convenient search service 36go.ru, you can apply for an appointment with the doctor you like at a nearby medical center at any time. To do this, just visit the company’s official website, enter brief data and wait a couple of seconds while the system independently selects the most optimal clinic options for you. For clients of our portal, we provide favorable discounts and promotional offers for examinations, which help save costs on scanning.
What is optical coherence tomography (OCT)?
The principles of optical coherence tomography were first explored at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the early 1990s. Carl Zeiss (Germany) created the first commercial version of a coherence tomograph in 1996. Currently, optical coherence tomography is an advanced innovative technology for visualizing the structures of the eyeball, without which no center of ophthalmology and eye microsurgery can do today. OCT of the eye is an easy-to-use, highly accurate non-invasive and non-contact technology that allows you to identify and monitor morphological changes in the tissues of the eyeball.
The method allows you to visualize cross-sectional images of the structures of the eyeball. You can study in detail the condition of the retina, the structure and features of all its layers, evaluate vitreoretinal relationships, and study the condition of the optic nerve and nerve fibers. High-frequency optical coherence tomography of the eye with an axial resolution of 3 μm allows intravital “optical biopsy” of intraocular structures of the eye. This resolution is tens of times more accurate than data obtained using ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging.
Operating principle of optical coherence tomography
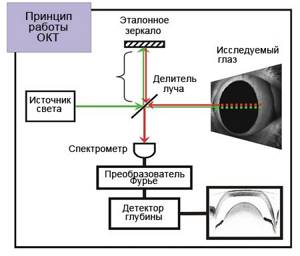
The essence of the tomograph is to measure the time during which a beam of light reflected from a particular optical section (A-scan) returns to the device. A series of A-scans performed on all structures of the area under study allows for reconstruction of both the anterior and posterior segments of the eye in the cross-sectional plane. Images of such cross-sections are called B-scans.
Due to the fact that the speed of light is very high, and the distance between the layers of the eyeball is very small (measured in microns), it is not possible to directly measure the transit time of light rays. For this purpose, the optical coherence tomograph uses low-coherence interferometry technology. During operation of the device, the emitted light beam is divided into two parts - the first beam of light is sent to the eyeball, and the second is a control beam and is directed to a special mirror surface. After reflection, both beams are captured by a special detector, after which the resulting data is analyzed and an image is formed. Using coherence analysis, the tomograph allows you to study even weakly reflective layers of the retina.
|
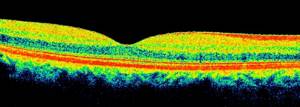
After the examination is completed, the computer generates an image that is available for analysis and interpretation by the attending physician. Depending on the ability to reflect light rays, all structures of the eyeball are painted in different colors on the resulting optical tomogram. For example, the vitreous body is black because it is a transparent, non-reflective medium. The anatomical structures of the eye, which have a high degree of reflection, give a red color or its shades on the tomogram. Weakly reflective structures are painted in cooler shades.
|
| Optical coherence tomography of the retina is normal |
Indications for optical coherence tomography of the eye
Ocular OCT provides the clinician with the ability to perform both qualitative (morphological features and reflectance) and quantitative (thickness, mapping and volume) analyzes of ocular structures in-situ in real time. Coherence tomography of the eye is indicated in the following clinical situations:
- verification of macular holes and pseudo-holes;
- diagnosis of epiretinal membranes;
- determination of the state of the vitreomacular interface: vitreoretinal relationships, vitreomacular adhesion, vitreoretinal traction syndrome;
- epiretinal fibrosis;
- retinal detachment, retinoschisis, maculoschisis;
- diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema;
- senile macular degeneration and choroidal neovascularization;
- assessment of optic disc parameters;
- early diagnosis of glaucoma and glaucomatous damage to the optic nerve;
- assessment and analysis of the structures of the anterior chamber of the eye, including the volume and thickness of the cornea.
However, despite the apparent universality of this method, assessment of the state of the organ of vision and diagnosis must be carried out based on the results of several examinations, including taking into account the clinical picture of the disease. Indications for each specific patient are determined by the attending physician based on individual clinical characteristics.
Brief information about the structure of the eyes

Its widened area is directed forward, and its narrow lobe faces the inside of the skull. By itself, it consists of an apple, muscles that help perform motor functions, tear ducts, a fatty membrane, a large number of vessels and nerves. The orbit is located next to the skull, nasal region, sinuses and nasopharyngeal cavity. It is necessary to understand that between the listed zones there is a rather complex connection that has an anatomical and topographical nature. Abnormal deformations in this area can originate here, and in some cases have the ability to move to other anatomical structures that are localized nearby. The described phenomenon leads to difficulties in examining the patient for the presence of painful conditions and the need to use quite serious scanning techniques, for example, computed tomography of the eyes.
What can you see with a CT scan of the eye?
When using the described method of testing the human body, specialists can detect the following pathologies:
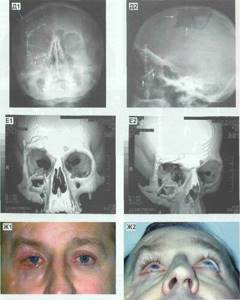
- Bleeding sites.
- Processes of vascular clogging.
- Inflammatory foci.
- Volumetric neoplasms of various etiologies.
- Foreign objects.
- Damage to soft parts.
- Deformations in the retina.
In order not to waste your personal time searching for a clinic where you can get an eye CT scan, use a simple and convenient portal specifically designed for selecting medical organizations based on the client’s preferences and wishes. 36go.ru was created in order to provide accurate and reliable information about the location of all city clinics involved in examinations, tell about the number of vacancies in the coming days, and also show current price lists for diagnostic activities.
In what situations is CT of the eye orbits prescribed?
Computed tomography is a modern technology that provides the most accurate and high-quality images about multiple pathologies occurring in the patient’s body at the moment. When contacting a doctor dealing with problems and complaints in the field of ophthalmology, a CT scan of the eye orbits may be prescribed in the following cases:
- If there is damage, both external and internal.
- When there is a foreign object inside the eye socket.
- In case of formation of inflammatory processes.
- The presence of secondary damage to the lacrimal glands or visual apparatus caused by abnormalities of an autoimmune nature.
- If there is a displacement of the apple towards the external cavity (exophthalmos).
- Formation of benign or malignant tumors.
In addition, the indications for performing a computed tomography include:
- Sudden loss of vision.
- Constant pain and discomfort.
3D visualization
Two-dimensional and three-dimensional visualization is possible. A three-dimensional image demonstrates diagnostic results much more accurately, which is why it is preferred. After starting the device, 50,000-100,000 images of eye tissue are taken within a few seconds, after which a computer program generates a 3D image. Thanks to this, it is possible to carry out the internal topography of the eyeballs with 100% accuracy.

Existing limitations for CT of the eye orbits
The described examination technique is a non-invasive way of studying the patient’s body and is one of the most popular techniques for studying various pathologies. But, despite the multiple advantages of the examination, there is a whole list of conditions in which CT scanning of the eye is prohibited. These include:

- Carrying a child throughout the entire stage of pregnancy - such a limitation is due to the fact that when scanning the body, the clinical device uses X-ray vibrations, which can adversely affect the further development of the fetus (it is worth knowing that when examining the orbital region, the dosage of toxic waves is 0.8 mSv, in contrast to computed tomography of the brain - 3 mSv).
- Children under 14 years of age - since the influence of X-rays can adversely affect the growing body.
Also, you need to understand that if a specialist prescribes a study for his patient with the introduction of an additional amplifier in the form of a contrast agent, then the number of contraindications increases significantly, with the following points:
- Individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
- Chronic kidney disease, liver disease, heart problems.
- The patient is in serious condition - connected to an artificial respiration device, comatose, etc.
With the diseases described above, it will take more time to remove all remnants of the contrast agent from the body, which will, in turn, cause intoxication, which will lead to serious side effects. In addition, if a nursing mother is prescribed an examination session with contrast, she needs to transfer the child to artificial nutrition for two days. If you don’t know where you can make an appointment for an examination of a similar plan, use a search service - use the search service 36go.ru. Our managers will help you decide on the choice of clinic, tell you details about any testing, and answer all your questions. To contact the company's operators, just call the hotline.
How is the procedure done?
First, the patient is placed comfortably on his back on a special X-ray table. A warning to keep the person still is usually sufficient, but this does not always work, especially with older patients. Therefore, in some cases, the laboratory assistant additionally secures the head using special straps.
Next, the head end of the table is moved under the scanner, which begins to rotate around the head to produce a projection of the eye sockets from different angles for a clear picture.
The incoming information is stored on magnetic tape, and the slice images themselves are projected onto a computer screen. Usually this is enough, but in case of unforeseen situations, the selected sections are also photographed. If contrast is further planned, the substance is administered after the first series of imaging, and then the procedure is repeated again.
Preparatory measures before CT eye
No special preparation is required from the patient before performing a CT scan. All you need to know is that when scheduling a health check with a booster, you will need to stop eating a few hours before your session (approximately 6-8 hours). There are no restrictions before the standard examination. You can eat regular foods, drink any liquid, take medications, etc.
More detailed information about diagnostics can be obtained on the official website 36go.ru. Our company was created specifically to help people find the most profitable and suitable option for a medical organization engaged in various testing methods. Using the services of the portal, you will receive information about available places for examinations for several days in advance, the current cost of the examination, and will also be able to read real reviews from clients who have visited different clinics.
Advantages of the method
First, the main advantage of retinal computed tomography
is non-contact, since the eyes are highly sensitive to any touch and interference. Secondly, the procedure takes no more than a minute (provided that no contrast is used). Thirdly, the diagnosis is absolutely painless (due to the fact that there is no physical intervention). Retinal OCT allows doctors to obtain detailed and clear information about the patient's eye condition, which is a definite advantage. Finally, this diagnostic method is quite inexpensive, its cost can reach 3000-4500 rubles.
Decoding the information received after completing a CT scan of the eye orbits
Computed tomography allows doctors to obtain detailed images of the required part of the patient’s body. The information obtained is interpreted by the doctor who conducted the assessment. To fully compile a report on the work done, on average it may take from 30 to 60 minutes. Data is placed on portable storage devices (flash cards, disk objects, etc.) or can be transferred to hand in the form of a printed photograph on wide-format film. The patient must check for the seal and signature of the radiologist.
Interpretation of eye tomography results
The tomography results are not only a three-dimensional image and layered images, but also various tables, diagrams and protocols. To decipher the results obtained, a specialist can use an additional database stored in the tomograph’s memory. As a result, the doctor receives data on the characteristics of tissues, the localization of thickening and thinning, the location of damage and pathologies, their size, and degree of development. In other words, all the necessary parameters to make a correct diagnosis.
How often can the examination be carried out?
The described body scanning technique is one of those diagnostic options that can only be done on the basis of strict instructions from a medical professional, since the tomograph produces toxic radiation that negatively affects the general condition of the patient. The dosage of radiation exposure in one session is a small amount, but with increasing repetitions of the examination, a cumulative effect may occur, which will have a detrimental effect on health. The most optimal repetition period is once a year. In case of serious problems, the doctor prescribes a scan every six months.