Treatment under the compulsory medical insurance policy is free!
Submit your application
Follow the news, subscribe to our social networks
Details
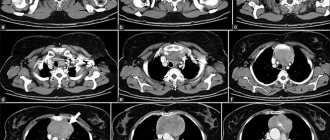
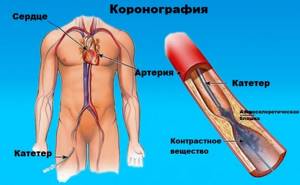
Cardiac coronary angiography is a procedure that uses a contrast dye, usually containing iodine, and x-rays to detect blockages in the heart's coronary vessels caused by plaque buildup. Blockages prevent your heart from receiving oxygen and important nutrients. This procedure is used to diagnose coronary artery disease, angina, sudden cardiac arrest, or abnormal results from tests such as a cardiac electrocardiogram (ECG) or stress test.
It is important to detect the blockage early because over time it can cause chest pain, especially after exercise or stress, and can also cause a heart attack. If a heart attack does occur, the doctor needs coronary angiography to plan further treatment tactics. Coronary angiography of the heart vessels is the most reliable method for diagnosing coronary heart disease (CHD), allowing one to accurately determine the location, degree, and nature of narrowing of the coronary artery.
Why is coronary angiography performed?
Coronary angiography is the most common of a group of procedures known as catheterization. It helps diagnose and treat various heart diseases. It is also called cardiac angiography.
A special contrast agent is injected into the blood vessels of the heart, which can be seen in an angiography unit using X-rays. It takes a series of images (angiograms), providing detailed information about the condition of the veins and arteries.
Preparation and technique
Your attending physician can tell you how coronary angiography of the heart is performed. The procedure is a minimally invasive procedure and requires preliminary preparation. Before hospitalization, a general blood test is required, the blood type and Rh factor are checked, and additional examinations may be prescribed.
The day before the procedure, it is forbidden to eat, so as not to cause vomiting and nausea during diagnosis.
The patient is taken to the X-ray endovascular surgery room. Since the manipulation is done under local anesthesia, the person is conscious. The next stage is piercing the artery. Usually the femoral artery is punctured in the groin area, but if there are difficulties with administering the substance, the puncture is performed through the radial artery of the arm.
After this, a catheter, which is a plastic tube, is inserted. The surgeon directs her to the coronary arteries. A person has two of them (left and right), so two catheters are installed and a special contrast agent is injected through them. It fills the entire space of the vessels, which makes it possible to visualize them. Using an X-ray machine, the doctor takes pictures in various projections and uses them to assess the patency of the arteries.
If no further surgery is planned, the catheter is removed. The puncture site is either sutured or glued, and sometimes a special bandage is applied. The duration of diagnostic coronary angiography is 15-30 minutes, and the duration of treatment is an hour or longer.
Subjects do not feel anything during the procedure. If it is not performed for the first time, there may be an unpleasant feeling in the place where the painkiller was administered, since the drug may act worse again. The cost of the manipulation is quite high, but due to its diagnostic value it is quite justified.
Postoperative period
After completion of the examination, a gentle regimen is recommended. It is advisable to limit movement of the limb into which the catheter was inserted. Contrast agents are toxic, so drinking plenty of fluids is encouraged.
In general, the effect of this method on the body is not felt, but it should be remembered that if the puncture site changes (redness, pain or other symptoms), you should immediately consult a doctor.
Indications
Coronary angiography of the heart vessels is an invasive research method, and therefore is carried out strictly according to indications. Indications for coronary angiography:
- Forms of coronary heart disease that are difficult to respond to drug therapy.
- For symptoms of angina pectoris, if the appearance of pain cannot be explained by other types of diagnostics;
- Unstable angina;
- The examination is prescribed after a myocardial infarction;
- Emergency coronary angiography is performed when there are symptoms of a heart attack (in the early stages of a heart attack).
- Some pathologies of the valve apparatus.
Coronary angiography of the heart vessels is prescribed to patients at vascular risk on the eve of surgery. Sometimes, with the help of angiographic examination, it is possible to identify vascular diseases that occur in a latent form.
How to prepare
Coronary fluoroscopy is performed after preparing the patient. The procedure can be emergency or planned. Emergency diagnostics are carried out with minimal analyzes and tests; the type and number of such checks is selected by the attending physician depending on the situation. For routine examination the following is prescribed:
- consultation of specialists: neurologist, cardiologist, surgeon;
- blood tests: coagulability, Rh factor and group, biochemical analysis;
- fluorography;
- allergy tests;
- Analysis of urine;
- electrocardiogram.
A full list of examinations is prescribed based on the clinical picture. The procedure is performed on an empty stomach to avoid nausea and the gag reflex. If the contrast agent will be injected into the thigh, you will need to remove hair from that area the day before.
A few days before the scheduled examination, the patient is shown a large amount of water, alcohol is prohibited. You cannot eat on the day of the event.
Before the examination itself, you need to warn the doctor about what medications you took and how you feel. You also need to take a change of clothes and personal hygiene items for your stay in the hospital.
How is coronary angiography of the heart performed?
- It is carried out strictly in a specially equipped operating room! A type of study - computed tomographic coronary angiography or CT coronary angiography, requires the presence of a computed tomograph.
- On the eve of the study, the patient undergoes a series of tests to ensure that the procedure is safe.
- The doctor will tell you in advance how to prepare for the examination. Read more about preparing for cardiac angiography in the following article.
- Basically, the research is carried out as planned. Urgent coronary angiography of vessels is performed in acute coronary syndrome and myocardial infarction.
- Coronary angiography takes from 15 to 30 minutes, but sometimes the time increases due to various circumstances.
- According to indications, coronary angioplasty and vascular stenting are performed simultaneously with coronary angiography.
Contraindications
Coronary angiography of the heart is a surgical examination. It, like any intervention, has a number of contraindications.
There are no absolute contraindications to the procedure. However, it is not recommended to carry out it in case of elevated temperature or the presence of symptoms of intoxication (nausea, vomiting, weakness, etc.), in the acute course of certain diseases (diabetes, heart and kidney failure, lung diseases).
The injected substance may cause allergies, so the doctor must make sure that the patient does not have such a reaction to the contrast.
The procedure should be prescribed with caution to people with low potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia) - it can cause arrhythmia.
The above contraindications are relative, therefore, it is possible to carry out such a diagnosis, but only after the condition has normalized.
Procedure
- You lie on your back on the angiography table. The X-ray imaging device moves around the head and chest and records from different angles (views).
- A special catheter is placed intravenously in your arm. They will administer sedatives to make you relax. During the angiography, you will be awake and able to communicate with the doctor and follow his instructions. During the coronary examination, you may be asked to take a deep breath, hold your breath, cough, or place your hands in various positions.
- Electrodes on the chest allow the doctor to monitor cardiac activity throughout the entire period. The cuff on the arm measures blood pressure, and the pulse oximeter shows the oxygen content in the blood. You will be given special medications (anticoagulants) to prevent blood clots from forming in your catheters and arteries.
- The area of the body (on the arm or leg) where the catheter will be installed is treated with a special solution, then local anesthesia is performed. The doctor makes a small incision (about 3 mm) at the access site and inserts a small plastic tube (introducer) into the artery. The catheter for coronary angiography of the heart vessels is inserted through the tube and carefully delivered to the coronary arteries.
- Passing the catheter does not cause pain and you will not feel its movement throughout the body. Make sure of this by reading patient reviews. Tell your doctor if you experience any discomfort during the angiography.
- The contrast agent is injected through the catheter. When this happens, patients notice warmth. During the operation, “jumping” heart contractions (extrasystoles) are a common occurrence; there is no need to worry about this.
- The contrast agent is visible on X-ray images, and by the way it passes through the blood vessels, the doctor will determine the exact location of the stenosis or occlusion and the severity of the affected area. Watch a video of coronary angiography here.
At the end of coronary angiography, the sheath is removed from the arm or leg and the incision is closed using manual pressure or a special device. You will be transferred back to the ward for further observation. You will lie down for several hours to prevent bleeding from the access site.
You will go home the same day if you had an outpatient coronary angiography. If the study was performed through the femoral artery or complications arose during outpatient coronary angiography, you will have to stay in the cardiology clinic until the morning or longer. It is recommended to drink more than usual (about 2 liters of water), unless there are contraindications, so that the contrast is eliminated from the body faster. The doctor will tell you when to resume taking medications and return to work and normal lifestyle. Avoid excessive strain and lifting heavy objects for several days.
Is this examination dangerous?
Everyone who is about to undergo this procedure is interested in what the consequences and complications may be. This type of diagnosis is considered a safe manipulation; the process is controlled using an X-ray or computed tomograph. Nevertheless, the risk of complications is still present; the most dangerous consequence is damage to blood vessels by the catheter.
The likelihood of such a complication is very low; it can occur from sudden movements or carelessness of the doctor. If the patient has not undergone proper preparation, an allergic reaction or bleeding may occur (with poor clotting). All these risks can be reduced if you carefully prepare and relax before the procedure.
If you are overcome by fear and anxiety in the X-ray operating room, you can warn the doctor about this and he will prescribe sedatives.
Contact your doctor immediately if...
- There is bleeding, new bruising, or swelling at the access site.
- Increased pain or discomfort in the area where the catheter was placed.
- Signs of infection develop, such as redness, discharge from the access site, and fever.
- Change in temperature or color of the leg or arm where the cut was made.
- Feeling of severe weakness.
- Have chest pain or shortness of breath.
If there is severe bleeding from the access site, apply a pressure bandage above the site and call emergency medical help immediately!
After research
After coronary angiography, the patient is transferred to his department, if the study was performed using radial access (through the arm) - in the Federal Research Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia, 99% of coronary angiographies are performed using this access - he almost immediately returns to his usual mode - he can sit down, stand up, and walk. The bandage that is placed at the site of the artery puncture is removed the next day.
For normal recovery of the body after the procedure, it is important to drink plenty of fluids. This will help remove the contrast agent from the blood faster. You should not endure the feeling of hunger. Be sure to ask your doctor when after coronary angiography you can take food and medications that were stopped before the study.
After discharge from the hospital, the patient must adhere to the following recommendations for 24 hours:
- give up heavy physical activity and intense sports;
- avoid psycho-emotional stress and stress;
- monitor the puncture site, which may still be painful for some time after coronary angiography.
It is important to understand that strict adherence to all specialist advice regarding the recovery period will allow the patient to quickly return to normal life. Therefore, you should strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations and not neglect his instructions.
results
- Coronary angiography will show the doctor with X-ray precision what is wrong with the blood vessels.
- It will become clear how many coronary arteries are closed or affected by atherosclerotic plaques.
- The exact location of the affected areas will be known.
- To evaluate the result of previous cardiac surgery: coronary artery bypass grafting or stenting, cardiac angiography is the best way to do this.
- This information will help your doctor determine which treatment for coronary artery disease, heart pain, or other disease is appropriate for you, and what health risks your heart condition poses.
Find out the prices for the coronary angiography procedure at the Endovascular Surgery Clinic by clicking on the link.
Price
Today, coronary angiography can be done at the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia in Moscow, a modern center that has everything necessary to conduct high-quality and informative diagnostics at the most affordable price.
Coronary angiography with ventriculography
38 500 ₽
It is important to understand that timely examination with the help of innovative equipment will allow us to timely determine the presence of disorders of the cardiovascular system and prevent the occurrence of life-threatening complications.
When is MR coronary angiography performed?
MRI allows you to:
- Contractility assessment
- Assessing perfusion at rest
- Stress perfusion assessment
- Assessment of delayed contrast enhancement
MR coronary angiography during a heart attack is impractical, since if a heart attack occurs, urgent diagnostic and therapeutic measures are needed, and MRI is a long-term study, unacceptably long in this case. CT angiography is ideal in this case, which takes only a few seconds.
The purpose of MRI is to assess the condition of the arteries of the heart, their stenosis and spasm, structural features, variations in location and branches, as well as changes in their condition after exercise and/or combined disturbance of the blood supply to the heart muscle under load conditions.
Advantages of non-contrast examination in cinema mode:
- Visualization of myocardial movements
- Visualization of turbulent and pathological blood flows
- High contrast between tissue and cavity structures of the heart
- No need to use contrast media
- Obtaining functional data (EF, LV volume, myocardial mass, etc.)
Advantages of contrast research:
- assessment of delayed myocardial contrast accumulation
- identification of areas of myocardial akinesis (lack of movement)