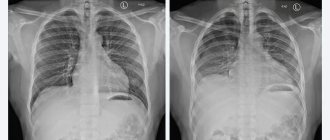
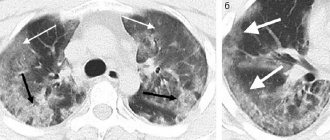
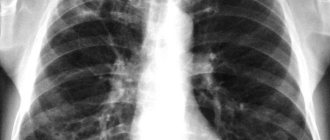
Computed tomography (CT) for coronavirus shows areas of infiltration and inflammation of the lungs - viral pneumonia.
It is the lungs that bear the brunt of the new coronavirus infection COVID-19 (or SARS-CoV-2).
Lung tissue has ACE2 protein receptors to which the virion attaches, thanks to robust protein spikes, similar to the SARS-CoV-1 pneumovirus first discovered in bats.
In addition to suffocation and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the high risk of mortality from COVID-19 is associated with other non-pulmonary complications: myocarditis, thrombosis of internal organs, and disseminated intravascular coagulation. However, CT scans show lung damage in 92 out of 100 Chinese patients hospitalized for coronavirus, according to Wuhan University of Technology. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) poses a great danger to life and health - it is an extensive bilateral inflammatory process with polysegmental foci of infiltration, which leads to pulmonary edema and acute respiratory failure.
The coronavirus enters the human body through the nasal cavity, mucous membranes of the eyes or mouth and, when it reaches the lungs, provokes an extensive inflammatory process in most patients - the alveoli (air bubbles of the lung tissue) are filled with liquid exudate or connective tissue. Doctors see these affected areas of the lungs, no longer involved in the respiratory process, on a cross-sectional CT scan of the lungs in the form of “ground glass”, a “cobblestone pavement” symptom. Also, coronavirus is often accompanied by pleural effusion.
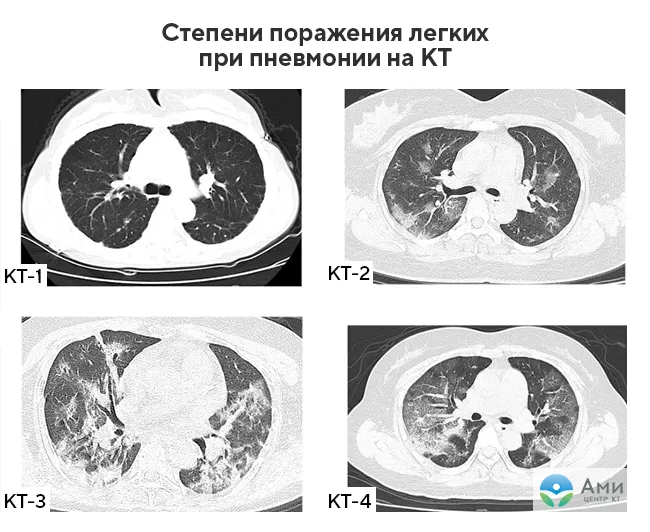
Based on the tomography results, the severity of the disease is also assessed, that is, the degree of lung damage: CT-0, CT-1, CT-2, CT-3, CT-4. Read more about the “pattern” of coronavirus pneumonia and the diagnostic capabilities of computed tomography in this article.
When is it necessary to do a CT scan of the lungs for coronavirus?
Usually, if viral pneumonia is suspected, a CT scan of the lungs is prescribed by the attending physician - a general practitioner or an infectious disease specialist. Sick patients do not need to wait up to 14 days for PCR results - tomography will show even minimal lung damage (up to 5%), while the pattern of pneumonia caused by coronavirus is visible quite clearly. A CT scan of the lungs is recommended to be done on days 5-7 of the onset of symptoms of acute respiratory disease.
The key difference between computed tomography and x-rays is that a CT scan shows the first degree of lung damage (up to 25%), and based on the examination results, a differential diagnosis is possible, that is, based on a specific clinical pattern on a CT scan, you can distinguish coronavirus pneumonia from bacterial or any other the other without laboratory diagnostics. However, not all patients infected with coronavirus develop lung damage with characteristic symptoms.
A CT scan of the lungs is recommended if the following symptoms are present:
- High temperature (more than 37.5°);
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath;
- Cough;
- Sensation of squeezing in the chest;
- Low level of blood oxygen saturation (less than 95%) according to pulse oximetry results;
- Increased fatigue, weakness.
Patients with severe symptoms and suspected coronavirus do not need to wait for PCR diagnostic results. Computed tomography will show foci of inflammation and infiltration of the lungs, fibrosis, and the degree of their prevalence. Thus, the patient will be able to begin treatment without wasting time under the supervision of the attending physician. Lung involvement of more than 50% according to CT results may be an indication for hospitalization.
Important! If you have the above symptoms, there is no need to wait for the results of a coronavirus test to check your lungs with a CT scan. The advantage of computed tomography of the lungs over x-rays and fluorography is that the diagnosis will show inflammatory processes even when they have just begun (5-7 days from the onset of acute respiratory infections symptoms).

Do I need to prepare for the procedure?
There is no need to prepare specifically or for a long time for a tomography session, but when going for a scan, it is important to consider the following points:
- Interaction with the device occurs in a lying position, so it is better to wear loose, comfortable clothes that do not restrict movement when lying on a high couch.
- All foreign objects, metal jewelry, and small change must be removed from the body and pockets, as distortions and artifacts may appear in the photographs.
- Tell the specialist about chronic pathologies, possible pregnancy, the presence of built-in implants, electronic stimulators.
- To register or conclude an agreement for the service, bring your passport, as well as the results of other studies and a referral from the treating doctor.
If the session is planned in a contrast mode, the last meal before the start of the procedure should take place no later than 2-3 hours. It's best to have a light snack to avoid feeling dizzy or nauseous while the dye is being injected intravenously. However, you should also not overeat, so as not to have the same effect due to the fullness of the stomach in a supine position.
Lung damage due to coronavirus
In 2021, an empirical lung visual assessment scale was developed, in which CT-0, CT-1, CT-2, CT-3 and CT-4 correspond to the stage of the disease and, accordingly, the degree of lung damage.
The doctor examines each lobe of the lung (5 in total) on cross-sectional scans in the transverse and frontal planes and assesses the volume of damage to each on a five-point scale. If there are no signs of inflammation, the radiologist assigns a value of 0 and so on. If inflammatory foci and infiltrates are present in several segments, such pneumonia is called polysegmental. With coronavirus, patients are most often diagnosed with bilateral polysegmental pneumonia. If you seek medical help promptly, the spread of infection in the lungs can be stopped.
Degree of lung damage due to coronavirus on CT
At the conclusion of a CT scan of the lungs, patients see abbreviations: CT-0, CT-1, CT-2, CT-3 and CT-4 What do they mean?
- CT-0 - no foci of inflammation and infiltrates are identified, the lungs are “clean”;
- CT-1 - lung damage up to 25%;
- CT-2 - lung damage 25-50%;
- CT-3 - lung damage 50-75%;
- CT-4 - lung damage > 75%.
According to the study “Time Course of Lung Changes at Chest CT during Recovery from Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) ,” published in July 2021 in the international journal Radiology, maximum lung damage (peak pneumonia) in most patients is observed on the 10th day of the disease . The sample did not include patients with specific complications, such as ARDS, cardiogenic pulmonary edema, thrombosis, the severe consequences of which are unpredictable.
What does coronavirus look like on a CT scan?
With coronavirus, CT scans clearly and clearly visualize infiltrates in the lungs - areas filled with exudate (fluid, blood, pus), as a result of which breathing is difficult.
They are especially clearly presented in the 3D reconstruction of the respiratory tract. This image is obtained after computer processing of the scans. This data is also written to disk, and the patient can view an image of his own lungs.
According to current research published in the journal Radiology, viral pneumonia caused by COVID-19 most often appears on CT images as bilateral ground-glass opacities and thickening of the lung tissue, such as thickening of the alveolar septa. On tomograms, on the contrary, these are lighter areas, since they indicate increased density of the lung tissue, and it transmits X-rays less well.
The presence of a single ground-glass lesion in the right lower lobe of the lung can be interpreted as the initial, very first manifestation of viral pneumonia.
O are not a specific sign of pneumonia due to coronavirus. This sign is characteristic of tumors, hemorrhages and other infections. Based on the results of a CT scan of the lungs, only a primary differential diagnosis of pneumonia (bacterial, caused by pneumococcus, fungi, etc.) is possible. The “pattern” of these diseases may vary only slightly. In order for doctors to make a correct diagnosis, the patient should undergo additional examination, for example, PCR. Laboratory diagnostics will help identify the specific causative agent of pneumonia.
As the disease progresses to a later stage, the pattern becomes more specific. Coronavirus pneumonia on a CT scan of the lungs is determined by the following signs.
What may be in the results
The scans produced by the equipment are immediately sent to the doctor’s computer, who studies them in detail after the procedure. The interpretation takes from half an hour to a day, so it is not necessary to wait for the results in the clinic. It is enough to leave your contacts at the reception so that you will be notified of readiness or a digital version of the conclusion and photographs will be sent to your email address.
In the photographs you can see clear boundaries of the internal organs, blood vessels and bones. The denser the fabric, the lighter it appears in the images. The pulmonary parenchyma is normally homogeneous, gray, but with the development of inflammation, fibrosis, and filling of the alveoli with fluid, the pattern changes. Foci of compaction are displayed in the form of a lightened network, “frosted glass”. Tumors and other neoplasms are also visible with precise sizes and configurations; they are indicated by a developed vascular network around the pathological object.
Frosted glass for coronavirus
“Frosted glass” is considered the main sign of lung damage in pneumonia. This is the name given to areas of lung tissue in which the alveoli are filled with fluid - these are infiltrates. The name refers directly to the visualization of this sign during radiological diagnostics. Seals of the “frosted glass” type resemble a whitish coating, the lung tissue is light.
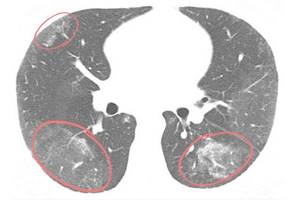
“Frost glass” with coronavirus is usually localized on both sides (bilateral pneumonia) in the lower and lateral sections, closer to the pleura or concentrated around the bronchi. At the same time, the visibility of the vessels, bronchi and their walls is preserved. The degree of lung damage is determined by the number and size of infiltrates.
Advantages over other technologies
Despite the large number of diagnostic procedures, lung CT is most often the method of choice. This is due to the following advantages:
- comprehensive visualization of the study area;
- Possibility of shooting from different angles;
- no blind spots;
- obtaining complete results in just one procedure;
- high accuracy, maximum scan resolution;
- detection of early stages of serious diseases;
- the presence of metal and electronic stimulators is not a serious contraindication to the study;
- construction of three-dimensional models of the organ with subsequent mathematical analysis of the data.
It should be noted that there is increased accessibility for all categories of patients. In comparison with alternative types of tomography, computer screening is one and a half or more times cheaper than MRI or PET, while in terms of information content regarding the lungs it is in no way inferior to them, and sometimes even surpasses them in certain indicators.
Cobblestone sign
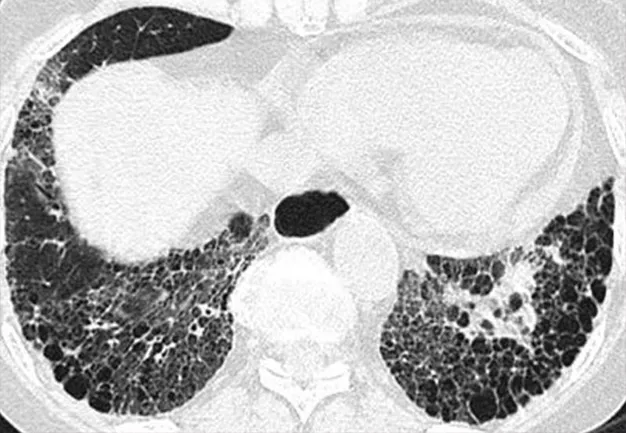
The cobblestone sign is also called the patchwork sign. Lung tissue on tomograms is visualized in the form of cells and resembles paving stones. This pattern is observed when the interalveolar septa are thickened. Extensive inflammation affects the interstitium, as a result of which it becomes denser, metabolic processes in tissues are disrupted: proteins and lipids accumulate in the alveoli, and the air space is reduced.
The symptom of “cobblestones” in combination with “frosted glass” indicates a severe, peak stage of pneumonia. Observed on days 10-12 of the disease. With favorable resolution, it resolves within 14-30 days.
Features of chest CT with contrast
In most cases, the native (standard) research mode is sufficient to detect the causes of the disease, but certain situations require strengthening the already informative procedure. We are talking about the use of contrast - intravenous administration of a coloring agent created on the basis of iodide solutions. When examined on a tomograph, iodine-filled cells appear stronger, become more noticeable and more contrasting. This is especially true for the circulatory system, since first of all the dye enters the vascular network and spreads throughout the body.
A CT scan of the chest with contrast takes a little longer than a regular study, as time is added for an additional manipulation - intravenous injection. You will also have to wait a few minutes until the dye disperses throughout the tissues and accumulates in inflamed areas and places of possible tumor growth. The safety of the drug used has been proven by many years of testing, but in some cases allergic reactions are possible. To avoid complications, it is better to do an immunological skin test for iodine tolerance in advance, consult a doctor about other personal contraindications and get a direct referral for scanning.
Symptom of air bronchogram
Air bronchogram is an X-ray term that means that against the background of dense and airless lung tissue with infiltrates (“ground glass” with consolidation), air space is preserved in the lumen of the bronchi. This part of the respiratory tract is fully or partially visualized on CT.
On the one hand, an air bronchogram indicates the patency of the proximal airways, on the other hand, it indicates large-scale obstruction of the lungs, in which there is practically no alveolar air.
Symptom of pleural effusion
Pleural effusion is an accumulation of liquid exudate in the pleural cavity. The pleura is a serous membrane that covers the surface of the lungs and the inside of the chest. Pathological fluid accumulates in the space between the lungs and the chest. Normally, it contains a little liquid, about 3-5 ml, - it is necessary for shock absorption and reducing friction of the respiratory organ on the ribs. The extra fluid makes breathing difficult and causes compression of the lungs.
Important! Only a radiologist can interpret the results of a lung CT scan. Computed tomography shows lung damage due to viral pneumonia. To reliably determine the type of infectious pathogen of pneumonia, the patient should undergo PCR.
Which is better to choose MRI or CT of the chest?
The appointment of one or another type of tomography is carried out by a specialized specialist, based on the individual indications and contraindications of a particular person. On computer screening, hollow organs and formations, as well as fluid-filled objects (large and small vessels, cysts, etc.), are better visible. Chest CT is not affected by minor movements during imaging, for example, dynamic pulsation of the heart during beating or contraction of the lungs during inhalation/exhalation. During scanning on a magnetic resonance imaging unit, displacement artifacts often occur due to such movement. This type of research can be used when studying soft tissue structures in the sternum. In general, experts consider the two different types of tomography to be complementary.