Patients who need an MRI procedure often wonder what the difference is between magnetic resonance imaging and radiographic examination, and why they need this particular procedure. Many people believe that there are no significant differences between these diagnostic methods, but this is not at all true. The characteristic features of each method and how they differ from each other will be discussed in this article.
MRI or x-ray examination
Let's figure out what these definitions mean and what features these two types of diagnostics have.
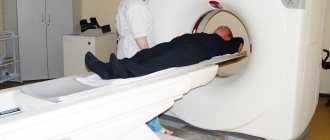
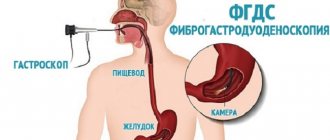
Magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) is a method of obtaining layer-by-layer images of internal organs and tissues. The technique is based on the use of a magnetic field. The tomograph generates a constant magnetic field. Thanks to a special combination of waves, atomic nuclei are excited in the human body. Their response is measured by the machine, and an image of the internal structures is obtained.
Radiography (or x-ray) is a method of obtaining a projection of the internal structure of organs using x-rays. They pass through the human body with varying degrees of attenuation, depending on the density of the tissue being examined, and are projected onto paper or film. This way a black and white photograph is obtained. The lighter the image on it, the denser the fabric.
Now let’s move on to assessing which is better, X-ray or MRI, consider the pros and cons of the methods and how they work.
Difference between MRI and X-ray
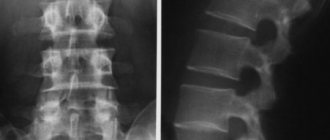
The differences between these methods are significant both in price and in the complexity of the equipment. Both examinations should show the projection of the internal organs on paper. In the case of X-rays, the same rays are used; dense tissues do not let them through, while soft tissues let them through with a slight change. Thus, on paper we see bones painted white, but internal organs, such as the lungs, appear dark. This method perfectly shows a fracture - quickly, simply and cheaply.
MRI is more complex both in hardware and in understanding. The principle of operation is based on the fact that there are many hydrogen atoms in the human body, which respond when in powerful magnetic fields, and by how many there are, a picture is obtained: the lighter, the more atoms. For example, there is a lot of hydrogen in the brain, and it will appear almost white. MRI is more accurate than x-rays, and it is easier for the doctor to find the cause of the patient’s complaints.
Limitations for MRI and X-rays
All diagnostic methods have contraindications. Thus, the restrictions for undergoing MRI are:
- ferromagnetic metal in the body (pacemaker, middle ear implant, metal implants, Ilizarov apparatus, hemostatic clips, tattoo ink with metallic inclusions, dentures);
- claustrophobia;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- kidney disease (during examination with contrast).
If you have no contraindications, then MRI is completely safe for you. Despite the large dimensions and noise, the harm from the device is the same as if you hold a magnet.
X-ray limitations include pregnancy, childhood (before puberty), and open pneumothorax. When using contrast, contraindications include: diabetes mellitus (in the stage of decompensation), pathologies of the liver, thyroid gland, kidneys, open type of tuberculosis. It is also not recommended to do this procedure too often. In addition, a general contraindication for both methods when using contrast is an allergic reaction in the patient to the components of the contrast drug. If radiography is performed infrequently, under the supervision of a physician and with the radiation dose recorded in the patient’s outpatient record, then the harm from ionizing radiation is almost eliminated. In this case, it cannot be said which is more harmful, X-ray or MRI. Both methods are quite safe. Especially if radiography is carried out in a well-equipped clinic using a modern device.
MRI, CT and X-ray: comparative characteristics
To understand the difference between CT and MRI, you need to mention the different physical phenomena and operating principles that are used in the equipment:
- Computed tomography (CT) and X-rays use X-rays. They allow you to assess the size, position, density of an organ, tissue and identify pathology by comparing it with normal values of healthy objects. The difference between a CT scan and an X-ray is that the machine scans the area under study multiple times. The doctor receives high-resolution images in three projections without shadows from overlapping organs. The information concerns the anatomical structure of organs and their physical characteristics.
- How is MRI different from X-ray? MRI uses a magnetic field to create detailed images of the body's organs and tissues. That is, a magnetic resonance imaging scanner causes a response from the water molecules in our body and uses this to create three-dimensional images. The technique analyzes the structure of tissues and provides the highest possible accuracy in diagnosing diseases of the brain, spinal cord, and oncology of various locations.
These methods complement each other and give doctors a comprehensive picture of the organs and tissues being examined.
What is safer - CT or MRI?
Safety can be assessed by comparing the number of contraindications. Because CT scans use X-rays, they cannot be done frequently and should not be used on children or pregnant women. But it is not contraindicated for people with metal prostheses, implants, or electrical devices.
MRI can be done for anyone who can lie still for a long time and is not afraid of limited space. RF pulses are completely harmless. The study can be carried out frequently and by anyone who needs it. However, there should be no metal objects, pacemakers, ear implants, or other gadgets on or in the patient’s body.
What is more informative – CT or MRI?
It is difficult to compare two methods based on different research principles. In addition, they solve different problems. Let's try to answer the question by studying the scope of application of two diagnostic methods:
- CT is indispensable for examining bones, tissues, and vessels of the head; it is extremely informative in diagnosing tuberculosis and pneumonia, examining the stomach, intestines, and other hollow organs. The method is used to examine the spine and bones, but it does not provide complete information when examining joints, ligaments, and soft tissues.
- Using MRI, neoplasms, tumors are diagnosed, and the membrane, tissues of the brain and spinal cord are examined. Diagnosing a stroke in the first hours helps doctors quickly take the necessary measures. The method is of great importance for identifying multiple sclerosis, diseases of the uterus, bladder, rectum, prostate gland, and oncology (development, localization of the tumor, degree of damage to neighboring tissues).
Which is better - X-ray or MRI?
In conventional radiography, X-rays pass through the area of the body being examined once perpendicular to the surface. As a result, the doctor receives a single-layer two-dimensional image, which clearly shows the most serious lesions. Shadows from neighboring organs can darken the image and reduce the quality of diagnosis.
MRI provides a layer-by-layer high-resolution image, reads the condition of joints, soft tissues, and their chemical composition. It is necessary for diagnosing diseases of the brain, spine, spinal cord, protrusions, and identifying oncology in the early stages.
Of the two methods, MRI is safer, since X-ray radiation must be dosed, and radiofrequency pulses are absolutely harmless. X-rays are prohibited from being used in examining children and expectant mothers, but MRI can be done as many times as needed without fear of radiation exposure.
The information content of each method is high. The data obtained allows the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis. Each method performs its own functions. They do not oppose, but complement each other. An experienced doctor knows which device is best to examine the lungs, which one is used to examine the brain or a spinal hernia, and when it is better to do both an X-ray and an MRI.
Advantages and disadvantages of both methods
Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of MRI. The advantages include the highest image quality, the resulting three-dimensional image, in which many organs and systems, areas of the brain with different slice thicknesses of 4-5 mm can be clearly seen. Such good visualization makes it possible to find tumors in different parts of the brain even at the earliest stages of their development. Another advantage is the safety of this research method, which allows you to repeat the procedure several times. Disadvantages include the higher cost compared to radiography and the length of the procedure, during which you need to remain motionless for a long time.
The advantages of radiography include simplicity, cost, and functionality. The disadvantage is relative unsafety. It is recommended to undergo such examination with significant breaks. The resulting image is static, which complicates the assessment of the condition. Without contrast agents, radiography of soft tissues is not very informative.
If we compare which is better, an MRI or an X-ray of the spine, for example, then even in this case it is impossible to answer for sure. It all depends on the damage. X-ray will allow the doctor to assess the condition of the bone tissue - to see fractures, cracks, etc. And MRI will visualize the nerves, spinal cord, surrounding soft tissues, and will allow to see the tumor.
Specifics of methods
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to diagnose the presence of pathologies in tissues. With its help, you can assess the condition of internal organs, soft tissues and vascular structures, as well as identify various tumors of a malignant and benign nature. Its main difference from X-rays is the ability to obtain scans of organs in the required plane and in three-dimensional form.
Radiography is used to diagnose pathologies of the skeletal system, as well as diseases that occur in soft tissues. This method is used to examine the abdominal organs and detect stones in the kidneys and biliary tract, as well as diagnose lung cancer, pneumonia and edema.
Make an appointment now!
When is MRI used and when is X-ray used?
These methods complement each other, and radiography is often used first. If it turns out to be insufficient, then they are sent for an MRI. For example, you have back pain, perhaps something wrong with your spine, and you are sent for an x-ray. If nothing is found, then you will be referred for an MRI, which may show, for example, a problem with the intervertebral disc. Another example. Your knee joint hurts. An X-ray shows that your knee is intact, but an MRI shows a torn meniscus. And one last example. You have severe pain in your arm, the doctor sends you for an x-ray, and it shows a fracture. Then additional diagnostics are not needed. However, only MRI is used to analyze the brain, as well as computed tomography (CT).
Dangers of MRI and X-rays
Danger during procedures exists only with radiography, because the patient is irradiated. This is not the case with MRI. Therefore, the answer to the question of which is safer, MRI or X-ray, is, of course, MRI.
The main differences between MRI and X-ray are as follows:
- An MRI of the lumbar region may take 15 to 25 minutes. It only takes a few seconds to examine the lumbar region using X-rays.
- The tomograph allows you to take an image in any plane. MRI is also distinguished by the ability to subsequently convert images into a three-dimensional model.
- MRI diagnostics are harmless to the human body, while the X-ray method produces serious radiation exposure.
- MRI allows you to see pathologies of microscopic size in soft tissues, radiography shows pathologies only in bone tissue.
Differences also appear in indications and contraindications. The best method for people with lumbar problems who have metal or electronic implants installed is an x-ray. When choosing between x-rays and tomography of the spine, you need to consult with specialists. If there is an inflammatory, degenerative or infectious process that affects bones and soft tissues, both examinations may be prescribed.
- MRI of the back muscles of the spine.
- MRI of the lumbar region.
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine.
Do I need an X-ray if I have an MRI?
The procedures are completely different when compared and provide different information about the state of the body.
Magnetic resonance and x-ray examination of the head
Both diagnostic methods are necessary and important. The main indications for MRI are:
- pathologies of the brain and spinal cord;
- suspicions of benign neoplasms, malignant tumors;
- vascular diseases;
- inflammatory processes of various localizations;
- infectious lesions of soft tissues;
- anomalies in the structure of organs, etc.
Tomography should be prescribed to clarify the diagnosis and identify hidden pathological processes.
Indications for radiography or CT are injuries, suspicions of the presence of stones or foreign bodies in internal organs. The method is widely used as a quick and good way to diagnose pathologies of the musculoskeletal system (spine, limb bones, etc.).
Patients often ask the question: “Do I need an X-ray if I have an MRI?” In some cases, the doctor prescribes both procedures in order to have enough information to exclude life-threatening conditions, identify serious diseases and select the optimal treatment tactics.
Ultrasound of the spine or MRI - which is better?
Ultrasound, like MRI, does not involve any radiation and can be performed on patients of any age. The advantage of ultrasound is greater availability and low cost compared to MRI.
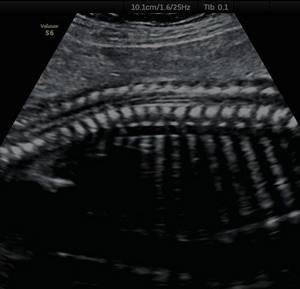
Ultrasound shows the size and location of intervertebral hernias, the condition of the discs, joints and adjacent vessels. This diagnosis is carried out if there is a suspicion of protrusion, osteochondrosis, narrowing of the spinal canal, defects in the development of the spine and vascular disorders.
Due to the inability of ultrasound to penetrate dense tissue, ultrasound of the thoracic region is not performed, which is a significant drawback of the method. Another disadvantage of ultrasound is the requirement for special preparation for diagnosing the lumbar region, since the study is performed through the abdominal cavity, and increased intestinal gas formation will lead to a decrease in the information content of the screening.
Also, ultrasound is based on the diagnostician’s subjective assessment of the picture seen, so the overall result of the study will depend on his qualifications and professionalism.
MRI does not have all these disadvantages. Along with the fact that MR scanning is characterized by the greatest information content and accuracy, its results can be recorded on a medium and transferred to any specialist for independent review of the study in controversial cases.
Preparing for the study
MRI does not require any special preparation for this examination.
For X-ray computed tomography such preparation is necessary. The day before the examination, foods that cause increased gas formation are excluded from the patient’s diet. First of all, this is black bread, pickles, fresh milk, etc. In the evening you should do a cleansing enema. The examination itself is carried out with the patient’s bladder full.
To optimize a CT or RT examination, you must take with you a referral from a specialized doctor, which indicates the preliminary diagnosis, goals and objectives of the examination. To assess the development of this disease, you should present the doctor with the results of previous examinations and available clinical notes.