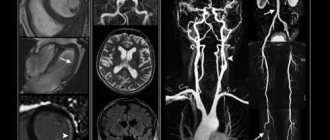
For more accurate diagnosis of cerebrovascular accidents, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are used today. These are research methods in which, using X-rays or a magnetic field, images of layer-by-layer sections of the brain are obtained, very similar to illustrations from an anatomical atlas.
These images can reveal changes in brain tissue. In medical terminology, the concept of “cerebral infarction” is used to designate the area of brain damage during a stroke. Indeed, the mechanism of damage is similar to a heart attack (myocardial infarction), but the clinical picture is different, since different organs are affected, and all symptoms are a consequence of a violation of their function.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging make it possible to clarify the nature of a stroke - ischemic or hemorrhagic, and also to distinguish a stroke from other diseases, such as a brain tumor.
What is a stroke
Stroke is an acute pathology of the brain, which is accompanied by thrombosis/blockage (ischemic stroke) or rupture of arteries, followed by intracerebral or subarachnoid bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke). The resulting acute cerebrovascular accident leads to cerebral edema, necrosis of areas of white or gray matter, and death of nerve cells. Symptoms of a stroke are a sudden severe headache, confusion and loss of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, paralysis of the limbs, etc. neurological signs. Acute cerebrovascular accidents are in 2nd place in mortality after coronary heart disease - about 6-7 million people die each year due to strokes. The most dangerous is hemorrhagic stroke with a mortality rate of 40%.
The main causes of strokes are atherosclerosis and hypertension. Cholesterol deposits in the walls of blood vessels impair blood circulation, promote the formation of blood clots, and reduce the strength and flexibility of the arterial wall, which easily ruptures when blood pressure rises.
Meningeal symptoms
Signs of irritation of the meninges can occur with parenchymal hemorrhage due to cerebral edema, but they are more characteristic of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
The most typical sign is a stiff neck, when the patient is unable to press the chin to the chest when lying down.
If the patient bends his knees while checking for rigidity, this is another sign of irritation of the meninges, which is called Brudzinski's sign.
Is it possible to do an MRI after a stroke?
Magnetic resonance imaging is not a contraindication for stroke if the patient's condition is stable and does not require intensive care and resuscitation measures, such as artificial ventilation. Moreover, the use of MRI in the diagnosis of acute cerebrovascular accidents makes it possible to clarify the diagnosis, identify the presence of blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques, and detect the source of hemorrhage. However, if the patient's condition is unstable and requires intensive care, magnetic resonance imaging must be abandoned in favor of the less accurate but faster computed tomography.
Magnetic resonance imaging for stroke is used not only for diagnosis, but also to assess the dynamics of recovery of the affected part of the brain after several days, weeks and even months. The method is ideal for this purpose, since computed tomography cannot be used with such frequency due to radiation exposure, and is inferior in accuracy to MRI.
General principles of treatment
After admission to the hospital, the neurologist assesses the severity of the condition, and then determines whether the patient needs to be operated on or whether it is better to treat him conservatively.
Many doctors agree that the most dangerous are the 3rd day after a vascular accident, and stabilization of the condition occurs on days 5-7-14, depending on the severity of the pathology.
Regardless of the type of stroke, treatment begins with:
- Bed rest.
- Elimination of any physical stress. For this purpose, laxatives and other symptomatic drugs may be prescribed, for example, antitussives for severe dry cough.
- Organization of patient care for the prevention of infectious complications and bedsores.
- Adequate nutrition depending on the level of consciousness: if the patient can swallow on his own, he eats gentle food through the mouth, if he cannot, through a tube.
- Prescription of drugs that regulate blood clotting. This is necessary to stop bleeding or prevent its recurrence.
- The use of neuroprotectors - medications that reduce the “suffering” of brain cells from oxygen starvation.
Medicines are prescribed only when they are necessary and not contraindicated.
Diagnosis of strokes using MRI
To diagnose a stroke, a standard magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is performed. The use of contrast makes it possible to increase the sensitivity of the method in controversial cases - symptoms similar to acute cerebrovascular accident can occur with tumors, a sharp decrease in blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus and other diseases.
Which MRI should I do for a stroke? If a stroke is suspected, the study is carried out in several modes, including necessarily in the angio mode to search for the vascular pathology that caused the disease (thrombosis, embolism, vascular aneurysm or vascular malformation, atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries).
Ischemic stroke
80% of all strokes are ischemic. The main cause of ischemic stroke is thrombosis of the cerebral arteries. Less commonly, the cause of acute cerebrovascular accident of the ischemic type can be a prolonged spasm of the arteries or a sharp decrease in blood pressure. Blockage of the artery supplying the corresponding part of the brain leads to the death of nerve cells and tissue necrosis. The severity of the condition is determined by which vessel was blocked, and what the areas of the brain that are in the necrosis zone are responsible for.
Signs of ischemic stroke on MRI of the brain
In the first minutes after a vessel is blocked, the cessation of blood flow to the brain tissue leads to ischemia or a lack of oxygen and nutrients. If the vessel was not completely blocked, and some part of the blood continues to flow, ischemia can persist for several hours or even days - this condition is called a transient ischemic attack. However, if the blood clot completely blocks the artery, within 5-10 minutes ischemia leads to the death of nerve cells and necrosis of brain tissue - an irreversible condition.
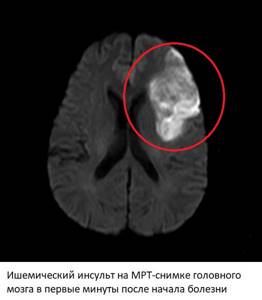
Changes on MRI after an ischemic stroke - in standard modes there are no obvious changes in the images, but in some modes (DWI, ADC) clear signs of ischemia and necrosis are visible within a few minutes after the onset of a stroke. In angio mode, you can detect a blood clot that is causing artery blockage, determine its location and extent, on which the prognosis will depend.
6 hours after the onset of acute cerebrovascular accident (ischemic stroke), structural changes begin to appear, visible in other MRI modes (FLAIR, T2). The equipment “sees” the area of the brain that has undergone necrosis due to tissue swelling. This picture persists for 1-2 weeks. After 3 weeks, the picture begins to return to normal, but the dead part of the brain will never be the same, which is partially visible in the pictures, regardless of how much time has passed. If necrosis occurs in areas of the brain responsible for speech, hearing, vision, and motor activity, restoration of the corresponding functions may take months and years or may never occur.
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic strokes or intracerebral hemorrhages account for 15% of all acute cerebrovascular accidents. The immediate cause is rupture of the cerebral arteries, weakened by atherosclerotic changes and increased blood pressure. Hypertension is one of the main risk factors for hemorrhagic stroke.
Signs of hemorrhagic stroke on MRI of the brain
Changes on MRI after a hemorrhagic stroke appear on the images within a few minutes after the onset of the disease. Magnetic resonance imaging has a separate mode (SWI) for detecting blood, which makes it possible to accurately determine the presence of hemorrhage in the brain. Moreover, the location, volume and extent of the hematoma have prognostic significance. In the vascular mode, cerebral arteries are detected, with obvious signs of atherosclerosis.
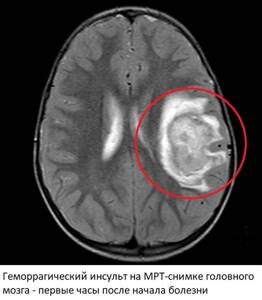
1-2 hours after the hemorrhage, the blood clots, which is why corresponding changes begin to appear in pictures taken in normal modes. The area of the hematoma changes, a ring appears around it due to cerebral edema and poor circulation. In the center there is a heterogeneous mass corresponding to a blood clot. This picture persists for several days or even weeks and corresponds to severe brain damage. In some cases, surgical removal of the hematoma is possible, but in practice, due to the high mortality rate (40-70%) and the serious condition of the patient, such operations are rarely performed.
Subarachnoid hemorrhages
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is one of the variants of hemorrhagic stroke, but the source of bleeding in this case is ruptured aneurysms of the arteries located at the base of the brain. The hematoma in subarachnoid hemorrhage is located between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater. Hypertension is also a predisposing factor.
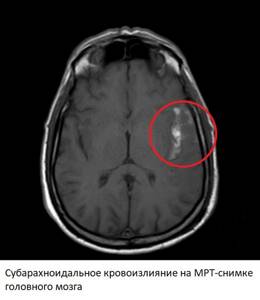
Changes on MRI after this type of hemorrhagic stroke are visible immediately after the onset of the disease (in SWI and FLAIR modes). Magnetic resonance imaging easily detects blood in the subarachnoid space. In angio mode, you can see the direct cause of hemorrhage - an aneurysm or other source of bleeding. In the first few days, MRI images may also show ischemic changes associated with reactive spasm of the cerebral arteries. As with hemorrhagic strokes, subarachnoid hemorrhage is visible in other modes within a few hours due to blood clotting.
Acute hypertensive encephalopathy
Acute hypertensive encephalopathy is a pathological condition that occurs due to high blood pressure (blood pressure above 200/130 mm Hg, less often at lower pressure). It is characterized by the appearance of areas of ischemia in the brain tissue, up to the formation of microscopic hemorrhages. Normally, with an increase in blood pressure, a spasm of the small arteries of the brain occurs, but with acute hypertensive encephalopathy, this same spasm can become prohibitive, which leads to the appearance of areas of brain tissue that lack oxygen. A sharp expansion of spasmodic arteries leads to cerebral edema. Acute hypertensive encephalopathy is a harbinger of hemorrhagic stroke.
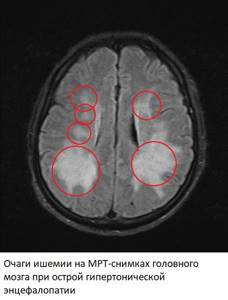
On MRI images, signs of hypertensive encephalopathy appear in the form of multiple foci of ischemia/microscopic hemorrhages in the brain tissue. In angio mode, spasm of some arteries and expansion of other arteries are simultaneously detected.
Rehabilitation in the intensive care unit
12-24 hours after a vascular accident, it is already possible to carry out restoration measures. Before they begin, a test is performed to assess independent swallowing, after which the patient’s feeding method is selected.
The following rehabilitation methods are used during the acute period of a stroke:
- Treatment by position. The position of the patient's head/arms/legs should be changed approximately every two to three hours, as well as turned to the side (if the condition allows it). In order to hold a person in a certain position, bolsters or pillows are used.
- Verticalization - giving the patient an upright position. This can happen passively (with the help of a functional bed or table), passive-active and active. However, to carry out this rehabilitation method, it is necessary to ensure the stability of the circulatory system. More often, verticalization begins in the neurological department.
- Breathing exercises can be carried out in various ways depending on the patient’s condition: vibration with the hands while exhaling, in a position that facilitates breathing, contact breathing (stimulation by touching the hands to the chest) and others.
- Therapeutic gymnastics includes assistance in restoring not only the large muscles of the limbs, but also the muscles of the neck and eyes. At the initial stage, passive gymnastics is performed, when flexion/extension of the patient’s fingers, arms and legs is performed by a qualified physical therapy nurse.
Also during this period, physiotherapeutic treatment is actively used: magnetic therapy, magnetic laser therapy, reflexology, electrical stimulation, darsonvalization and other methods.
What does an MRI show during and after a stroke?
Magnetic resonance imaging for stroke allows you to find out which part of the brain was affected by acute cerebrovascular accident, what is its extent, location and volume. Together with other prognostic signs, these data are important for subsequent prognosis and assessment of the patient’s condition, choice of treatment tactics and assessment of the results of therapy.
MRI is also excellent for follow-up of treatment results. The study can be repeated as many times as necessary for the doctor, without harm to the patient’s health. By observing changes in the images, you can evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment and, if necessary, make its correction. Everything that an MRI shows in a stroke can help doctors, including in preparing for surgical treatment.
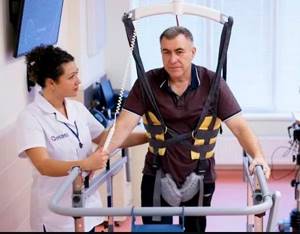
Rehabilitation in the acute period
At this stage (from 24 hours to 3 weeks), maintaining the achieved effect and improving exercise tolerance plays a significant role. For this purpose, methods such as:
- treatment by position;
- massage, which is equivalent to passive gymnastics;
- breathing exercises;
- active verticalization in the absence of contraindications (if necessary, using additional support);
- mechanotherapy;
- training on cyclic simulators.
During this recovery period, active correction of speech disorders is carried out with the involvement of speech therapists.
Causes of hemorrhage
Hemorrhage due to arterial hypertension
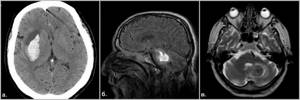
Fig.16
Hemorrhage due to cavernous angioma
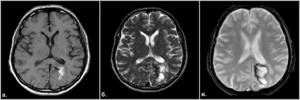
Fig.17
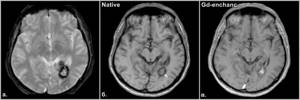
Fig.18
Hemorrhage due to cerebral amyloid angiopathy
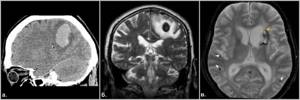
Fig.19