Tomographic research methods today are among the most modern and high-tech, so doctors are increasingly and for various clinical reasons prescribing CT scans of the abdominal organs. Screenings with layer-by-layer sections are carried out on equipment of different structures and in different modes. This affects not only the effectiveness, but also the cost of a computed tomography scan of the abdominal organs. It should be emphasized that a computer type of scanning is much cheaper than similar types of research carried out on other types of tomographs, so most patients can undergo it.
What is an abdominal CT scan?
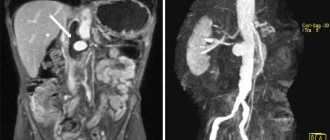
Unlike conventional radiography or a publicly available and cheap ultrasound examination, computed tomography of the abdominal cavity records the most informative data that helps to quickly and accurately identify a developing disease. In this case, the diagnosis of organs is carried out using special equipment, which consists of a massive tunnel or annular part, inside which the patient is placed on a transportable couch. Sensors built inside the installation scan the desired area, send the received data to a computer, where they are converted into numerous slice images with a slight indentation from each other.
There are two main research options: native tomography and diagnostics with contrast. The sharpest images are those taken in contrast mode. In this case, the session will take more time, the cost of contrast screening will also be slightly higher, but the information content of the examination also increases several times. During scanning, an X-ray field is used, which gives an ionizing load on the body of 5-7 m3V, but modern devices strive to minimize radiation exposure, so CT is a safe form of diagnosis.
If, for objective reasons, the patient needs to find an alternative to multislice computed tomography (MSCT), the attending physician determines which form of scanning would be appropriate: MRI of the abdominal organs or an angiographic form of research covering the vasculature - CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and its branches.
How does a contrast-enhanced CT scan differ from a conventional scan?
Contrast is an iodine-containing drug that, after being injected into the brachial vein, is distributed through the arteries and “colors” the vessels, lymph nodes, tumors and soft tissues that receive the blood supply in the images. Contrast makes visible damage to organs and blood vessels (malformations, blockages with atherosclerotic plaques), etc. On CT, primary conclusions can be drawn regarding the specifics of the detected neoplasm.
For the growth of a malignant tumor, more nutrition is needed, so the blood supply at the site of its localization will be more intense. CT with contrast reveals metastases - secondary foci of cancer.
When examining the abdominal cavity and pelvis on CT, it is important to exclude damage to internal organs, neoplasms and circulatory disorders.
Therefore, such studies are usually carried out with contrast.
What can be seen on MSCT of the abdominal organs
When going for a scan, the patient has the right to expect that the following pathologies can be detected based on its results:
- congenital deviations from the norm in the anatomy of the abdominal organs;
- growths inside the gastrointestinal tract (adenomas, polyps, fibromas);
- tissue death;
- tumor formations of different quality;
- inflammation and abscessive lesions;
- foreign objects penetrated naturally or as a result of injury;
- lymphadenopathy;
- consequences of hepatitis;
- narrowing of the biliary and urinary system;
- Cholango-pathologies.
Diagnostics can be expanded with the use of a contrast agent, as a result of which even microscopic and hidden inflammatory zones, early and precancerous stages of oncology become apparent. Since the session lasts no more than half an hour, and in the native mode – about 15 minutes, scanning becomes the best solution in emergency situations: with closed trauma to the abdominal organs, perforation of the appendix, strangulated abdominal hernias. The cost of screening in such cases does not change or is completely transferred to a free form of examination.
Methodology
With a CT scan of the retroperitoneum, the patient is placed on a special table around which the tomograph moves. To ensure clear images, the patient should not move during the examination. A retroperitoneal CT scan lasts 15 minutes; with contrast, the examination can take up to half an hour.
Contrast enhancement
A retroperitoneal CT scan with contrast is prescribed when the doctor suspects cancer or in a number of other cases. The method of administering the drug is chosen by a specialist. It depends on which part of the retroperitoneal space CT scan with contrast needs to be performed, and what the examination should show (which diagnosis to confirm or refute).
Contrast-type computed tomography
In the mode of tomography enhancement with contrast agents, iodine-based solutions are used. They are administered intravenously, spread throughout the body within a few minutes, and accumulate in larger volumes in those areas where there is an inflammatory process or tumor growth. An abdominal CT scan with contrast is then performed using the same equipment as the standard procedure. The cost is affected only by the use of consumables, as well as an increase in scanning time.
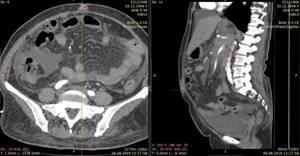
Images after contrast screening show areas “tinted” by the drug much more clearly, helping to identify a complex disease with less time wasted on diagnosis. A dye solution can be introduced both before the start of scanning and during the scanning process, if monitoring the distribution of the dye over time is required. The session in this case increases to 40 minutes. There are no special manipulations for removing the drug; it is released from the body naturally - through the urinary system over the next 48 hours.
Preparing for a computed tomography scan of the abdomen
To ensure that the effectiveness of the examination does not suffer, it is necessary to properly prepare the abdominal area for screening. Any studies of this area require “calming” the gastrointestinal tract, freeing it from feces and increased flatulence. To do this, the patient receives a list of recommendations for preliminary diet and medication. You should adhere to dietary restrictions for no more than 2 days before the procedure; the same amount of time will be required to take antispastic drugs and medications that reduce gas formation in the intestines. The patient is contraindicated:
- any raw vegetables and fruits;
- desserts fortified with fructose or glucose;
- dairy/fermented milk products;
- food and drinks based on primary fermentation.
The most commonly used medicines are Espumisan tablets or its analogues at a low cost. On the eve of the session, cleansing manipulations are carried out - taking laxatives, microenemas or water enemas. On the day of the examination, you need to go to the medical facility on an empty stomach, and you can drink some clean water two hours before. If there are spasms in the gastrointestinal tract, you need to take a couple of antispasmodic tablets half an hour before. It relaxes the intestinal muscles, which will allow you to get accurate scans of the area being studied.
Preparation
The preparatory stage for a CT scan of the abdominal organs begins 2 days before the diagnosis date with the transition to a diet that reduces gas formation. Legumes, fruits, white bread and confectionery, fermented milk products, kvass, beer, and carbonated drinks should be excluded from the diet. The menu these days can include eggs, porridge, boiled meat and steamed fish. To prepare the intestines on the day of the test, you can take 2 tablets of noshpa within 20 minutes. The tomography procedure itself is done on an empty stomach.
Leading doctors of St. Petersburg

Pashkova Anna Alexandrovna
specialization: MRI doctor, radiologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences. Appointment - at the AMI Medical Center, Standard MRI on Ladozhskaya
medical experience - 21 years
Online registration
Khalikov Aziz Jalanovich
specialization: MRI doctor, radiologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences. Registration - at MC Scandinavia
medical experience - 20 years
Online registration
Trufanov Gennady Evgenievich
specialization MRI doctor, MD, professor. Recording - Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center named after. V. A. Almazova"
medical experience - 35 years
Online registration
Kholin Alexander Vasilievich
specialization MRI Doctor Professor of the Department of Radiation Diagnostics Northwestern State Medical University Appointment - CMRT Staraya Derevnya, CMRT Petrogradskaya
medical experience - 35 years
Online registration
Interpretation of abdominal images
Only experienced diagnostic radiologists can interpret the resulting scans.
Specialist doctors can also identify obvious disease on tomographic sections, but it is better to rely on several opinions to know exactly what pathology of the abdominal organs the patient has. It is difficult to issue a conclusion immediately after completion of the tomography, since a targeted study of the images is required. Their number on different equipment ranges from 16 to 340 slices (and sometimes several times more). If the clinic’s specialists are not very busy, you can get a description in 30-60 minutes. If the clinic is very busy, results are issued the next day. They need to be taken to the treating doctor, who will make a final diagnosis.
Example
The conclusion, which is handed to the patient or his relatives, has a typical structure. An example of it can be seen in the following photo:

Descriptions of organs in which no pathology was found are brief and contain information that they have a typical shape, structure, size and location. The main attention is paid to the detected tumor, which is located at the base of the porta hepatis. It is noteworthy that the doctor does not indicate the type of tumor and does not call it “cancer” or another word . This can be done only after a cytological examination has been performed.
How to conduct a high-quality computed tomography scan
First of all, it is necessary to pay attention to the class and novelty of the equipment used in the tomography center. Modern medical institutions use spiral and multispiral installations with high scanning productivity. The greater the number of slices, the smaller the distance between them, which helps identify microscopic abnormalities. But for standard highly informative screening of abdominal organs, a 32-slice device is sufficient.
If doctors insist on using a contrast agent, you should not refuse it, since only in an enhanced mode are severe pathologies detected in the early stages of their development. Treating diseases in the early stages is easier and more productive than in an advanced state. It is also better to contact an institution where highly qualified employees work. The study of images of the abdominal organs should be entrusted to diagnosticians with long experience in this work. The patient can learn about the rating of the clinic he is visiting from reviews of other visitors. Our service also has this option. The cost of procedures in different organizations is also indicated here so that you can compare and choose the best options.
What does a CT scan of the abdomen cover?
In the abdomen and retroperitoneal space there are a large number of organs that are closely located and united into systems.
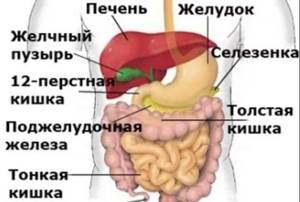
During abdominal screening, visual coverage of the following structures occurs:
- liver;
- spleen;
- pancreas
- adrenal glands and kidneys;
- upper zone of the ureters;
- gallbladder and its ducts.
If the intestinal loops are cleaned and are in a calm state, they are not visible in native diagnostics. The study can be expanded using a contrast solution. Then the large blood channels of the department will be clearly visible on the pictures. If a point pathology is found in a large sector of the abdomen, a targeted examination of a specific organ may be prescribed. The cost will be lower since the scanning scale is smaller. Many clinics also offer patients good discounts for repeat procedures.
Contraindications for CT of the retroperitoneum
Retroperitoneal CT is a noninvasive procedure that is considered safe for most patients. Contraindications include pregnancy or breastfeeding, the patient's inability to lie still - hyperkinesis.
For CT of the retroperitoneal space with contrast, relative contraindications will be diseases of the cardiovascular system, liver, kidneys and urinary tract, diseases affecting the condition of blood vessels. A CT scan of the retroperitoneum with contrast is not done in case of an allergy to the drug.
When is an abdominal examination required?
There is a large list of indications for diagnostics, the main part of which consists of the patient’s pathological complaints:
- suffered blunt or penetrating trauma to the abdominal cavity;
- blood flow within the gastrointestinal tract of varying intensity;
- severe pain;
- palpable neoplasms, signs of tumor growth;
- the presence of high fever accompanied by abdominal discomfort;
- complications after abdominal surgery.
For scanning, it is necessary to obtain a referral from the treating doctor, as the procedure has restrictions on its use. If there is no referral, but the patient wishes to conduct an examination on his own initiative, you need to consult with the radiologist on duty at the tomography center or with his specialized specialist. The cost of the consultation is determined additionally or is included in the package of the selected type of CT scan.
Contraindications to the procedure with contrast
To avoid complications, abdominal CT is not performed in patients with:
- allergy to iodine;
- severe renal failure with elevated creatinine levels in the blood (creatinine testing is included in the services of our diagnostic center);
- hyperthyroidism and other thyroid diseases.
Children over 12 years of age have their internal organs checked with contrast only according to indications with a doctor’s referral.
For women breastfeeding, the procedure is not prohibited. Radiation exposure does not affect milk, but the dye partially penetrates into it. Therefore, you will have to give up at least two consecutive feedings. Before the study, the woman must express and store the milk. After CT or MSCT with contrast, you must wait until the drug leaves the body and after two pumpings, feed the baby as usual.
Any questions you may have and the price for contrast examinations can be clarified with the administrator.
When is it prohibited to do a computed tomography scan of the abdomen?
You will have to choose another diagnostic option in several cases, most of which can be called conditional.
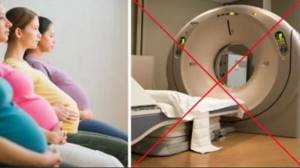
A complete refusal to screen the abdominal cavity using radiographic equipment will follow if the patient is pregnant or of insufficiently mature age. In these situations, increased ionizing radiation can harm the actively growing body of the fetus or child.
The procedure also has additional limitations that can be overcome if additional measures are applied and the scanning mode is changed. Complications may occur if the patient has the following:
- allergic reactions to iodine-containing medications or other components of the contrast solution;
- temporary or permanent urinary dysfunction;
- complicated course of asthma;
- severe diabetes;
- sudden panic attacks when placed in a confined space.
Modern installations allow for different patient weights, but difficulties may arise if the upper value of 120 kg is exceeded. To ensure that the tomographic check of organs does not end on the way to the equipment, find a clinic with equipment in your weight category in advance.
Conducting a contrast scan of the abdominal organs
After appointing a specialist, making an appointment for screening and preliminary preparation, the day of the examination comes. After registering at the clinic, the patient is escorted to a room with tomography equipment. You need to check your pockets in advance and remove metal and other dense objects from your body that could appear as artifacts in the photographs. Next, the following manipulations are carried out:
- Placement inside the scanner in a stationary position.
- Administration of a contrast agent, if provided for by the planned program.
- Scanning organs with installation sensors.
- Temporary breath holding at a separate stage of layer-by-layer shooting.
- Completion of the study and then awaiting the conclusion.
After screening, there is no need for rehabilitation, so the person being examined can immediately go about the remaining matters. There is no need to wait for the results at a medical facility. All you need to do is leave your contact details to send documents digitally by email.
results
Each patient receives examination results 30 minutes after the procedure. Some clinics offer the service of recording study results on a disk or flash drive. The quality of the image depends both on the tomograph itself and on the patient’s compliance with all the radiologist’s recommendations and his immobility during the examination. If all the rules were followed during a CT scan, the resulting image will clearly visualize, for example, the location and number of kidney stones or signs of thrombosis.
Yusupov Hospital offers services in various diagnostic methods. The diagnostic building has modern equipment. The device of a computed tomograph allows you to significantly reduce the radiation dose to the body and conduct the study as quickly as possible. At the end of the study, the patient receives a conclusion and ready-made images - in “paper” format, on a CD or in the form of an email.
The hospital has polite and attentive medical staff who create a comfortable atmosphere for the patient. Administrators are always ready to answer your questions. You can make an appointment by calling the hospital call center. Yusupov Hospital is a multidisciplinary center that provides qualified care to each patient on an individual basis.
Make an appointment
Cost of MSCT of the abdominal cavity

Prices for hardware diagnostics are based on various factors:
- cutting capacity and type of equipment;
- the need to use a contrast solution;
- time allocated for computed tomography of organs;
- availability and experience of receiving staff;
- periodic discounts, permanent loyalty programs.
In St. Petersburg clinics, computed tomography of the abdominal organs has different prices, which also depends on the location and rating of the organization. Average prices for abdominal examination are shown in the table:
| Name of procedure | Price | Possible discounts |
| Computed tomography of the abdomen | from 3100 rubles | At night from 00:00 to 07:45. |
| Computed tomography of the abdominal organs with contrast | from 4200 rubles | At night. Daily discounts for pensioners, disabled people, veterans, medical workers, students, mothers of many children up to 10%. |
| CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and its branches | from 4000 rub. | At night |
| CT angiography of the abdominal aorta and its branches with contrast | from 6000 rub. | At night |
Indications and prohibitions for performing computed tomography
Considering that tomography is directly related to the need to irradiate the body, such a procedure is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor in cases where there is an objective need for this.

Indications for CT scan of the abdominal cavity are:
- determining the need for surgical intervention or an already prescribed operation: this way the doctor receives the most accurate data on the degree of change in organs and the localization of such change;
- the appearance of acute pain, jaundice, sudden weight loss of unknown etiology;
- disruption of the urinary system;
- digestive disorder;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms;
- manifestation of liver diseases;
- suspicion of vascular disorders;
- control over the implementation of prescribed treatment;
- the appearance of symptoms of lymph node damage.
Some conditions and pathologies in humans completely exclude the possibility of examining the abdominal organs using a computed tomograph. For example, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, the use of X-ray radiation is strictly not recommended - it can harm the baby.
Some tomographs have a patient weight limit of 140-180 kilograms. If your body weight exceeds this mark, the procedure may be in question.
Conducting a CT scan of the abdominal organs, as well as other parts of the body and organs, is prohibited for patients under 3 years of age. Children of primary school age can be scanned using a tomograph, however, if possible, it is better to replace this research method with a more harmless one, such as MRI.
Diseases such as diabetes mellitus, acute inflammation of the kidneys, heart, liver, blood, are considered relative contraindications when conducting a study with a contrast agent - if they are present, the doctor, at his own discretion, decides whether the procedure is possible.
As for contrast-enhanced computed tomography, its contraindications, also associated with the administration of a contrast agent, are as follows:
- intolerance to iodine and iodine-containing drugs diagnosed in the patient;
- a history of allergies or severe forms of bronchial asthma;
- hyperthyroidism;
- diagnosed renal or liver failure of any kind.