Magnetic resonance imaging is a technically complex diagnostic procedure. MRI is prescribed when there is insufficient information obtained through routine studies to identify the causes of diseases, in case of a questionable diagnosis, to search for tumors, to monitor the effectiveness of operations. The advantages of tomographic scanning are safety, information content, painlessness, and no need for special preparation. The last point is not relevant for all types of research. When studying individual organs, preparation for MRI is necessary. Specific measures the day before may be required when planning contrast enhancement of images. There are special rules for preparing for an MRI examination when studying the abdominal and pelvic organs. Following your doctor's instructions will help you get accurate scan results.
Positioning the patient before MRI
How to prepare for magnetic resonance imaging?
The effectiveness of the study depends on the scanned area in question. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to study loose, fluid-rich structures. The method is used to diagnose diseases of internal organs, soft tissues, blood vessels, and joint elements. In some cases (fractures, damage to arteries and veins, stroke, multiple injuries, etc.) MRI may be uninformative.
The diagnosis is preceded by a consultation with a specialized specialist. The doctor will assess the need for the procedure, determine the advisability of contrast enhancement, and tell you how to prepare for an MRI.
To undergo the test, insurance coverage applies to specific medical institutions (indicated by the doctor when issuing the referral). In other cases, the choice remains with the patient. It is worth giving preference to specialized MRI diagnostic centers with powerful modern equipment. Examination of the brain and blood vessels using open tomographs will not provide the necessary information. The most detailed and accurate images are obtained using high-field devices with a power of 1.5 Tesla or more.
Conversation between doctor and patient before scanning
When making an appointment, a diagnostic center employee asks clarifying questions. Clinic staff must be notified of the presence of any foreign objects in the body:
- silicone implants with magnetic guides;
- pins, knitting needles;
- plates;
- vascular clips and stents;
- endoprostheses;
- electronic devices (pacemaker, nerve impulse generator);
- dental products (braces, crowns, metal inlays, etc.).
You will need to prepare a document about the composition and properties of the device (passport, extract from the card). If you have vascular implants, a certificate indicating the date of surgery is required. Patients with pacemakers, defibrillators and insulin pumps are not prescribed MRI, since exposure to a magnetic field can pose a threat to human life.
Whether preparation for an MRI is necessary should be checked with your doctor. A number of anatomical areas can be examined at any time. The latter include:
- head structures;
- neck;
- joints.
Preparation is needed when studying moving, hollow organs. In this case, the activities the day before are aimed at suppressing peristalsis and preventing the accumulation of gases, since these phenomena provoke the appearance of artifacts (blurred and illuminated areas) in the images, reducing the information content of the study.
Before MRI of the abdominal cavity, liver, pancreas, stomach, intestines, kidneys, you should follow a diet for 2-3 days and ensure natural bowel movements on the eve of the procedure. Before scanning the pelvic organs, it is necessary to correct the diet, have a bowel movement, and, in addition, adhere to the drinking regime. The procedure requires an average bladder fullness. You need to visit the toilet about an hour before the start of the tomography, and drink 1-2 glasses of water 5 minutes before the examination.

Fresh vegetables and fruits should be abandoned on the eve of tomography of the abdominal and pelvic organs
Indications
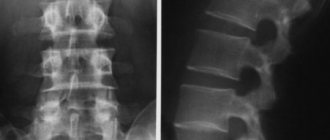
An MRI of the lumbar region should be done only if certain symptoms are present, as well as if there is a referral from the attending physician. Among those conditions that MRI of the sacrolumbar region shows, it is worth noting the following:
- Osteochondrosis in the chronic or acute stage;
- Injuries of various nature;
- The likelihood of developing a tumor process;
- Metastasis to the lumbosacral region;
- Acute paroxysmal or aching continuous pain;
- Suspicion of an infectious process;
- Inflammation, impaired blood flow, etc.
MRI: rules of passage
Simple preparation is necessary on the day of scanning. At the DC you need to take your passport and available medical documentation (referral, results of other diagnostic procedures, certificate for the implant).
It is better to come to the clinic 5 minutes before the appointed time. This will allow you to fill out the forms without haste. You should arrive 15 minutes early for your pelvic scan so you can drink extra water.
Preparation for an MRI procedure includes a preliminary consultation with a radiologist. The conversation helps to identify contraindications to scanning and clarify the purpose of tomography. The specialist is warned about:
- pregnancy (if you suspect, you should do a test);
- feeling unwell (due to a recent ARVI, cold, etc.);
- acute pain;
- drinking alcohol on the eve of diagnosis;
- fear of equipment or fear of confined spaces.
Before entering the diagnostic room, you should prepare for tomography: remove jewelry, metal products, and items of clothing with locks, hooks, or buttons. Personal items and gadgets are left in the dressing room.
In the MRI room, the patient lies down on the tomograph platform. To prevent movement, the subject's body is secured with soft straps. During the scanning process, you can communicate with a clinic employee via two-way speakerphone or give a signal by pressing a special button.
Is it possible to drink alcohol before a brain MRI?
Patients undergoing head screening should absolutely not abuse alcohol.
Alcohol provokes inappropriate reactions to external stimuli and does not allow one to get a real picture of what is happening in the central nervous system. Under its influence, the vessels first sharply expand and then contract, which is why it is not possible to display changes in brain tissue.
Attention! With chronic alcoholism, there is a possibility of edema forming, which will prevent the radiologist from seeing pathological changes.
What can you eat before an MRI?
When preparing for magnetic resonance imaging of any anatomical area, except the abdominal cavity and pelvis, it is allowed to consume familiar foods. There are no restrictions regarding the frequency of meals. It is better to refrain from eating exotic foods and overeating (to avoid causing indigestion), and not to drink too much coffee (to prevent frequent urination).
Before an MRI of the abdominal cavity and pelvis, you need to follow a diet to prevent constipation and excess gas formation. 2-3 days before the procedure you should exclude from your diet:
- sweets;
- dairy products;
- baked goods;
- black bread;
- legumes;
- berries and fruits;
- alcohol;
- mushrooms;
- starchy foods (rice, potatoes, pasta).
You can eat meat, eggs, fish, cereals, stewed vegetables, day-old bread, biscuits. These same foods are allowed to be eaten on the day of the examination, taking into account the need to withstand fasting 4 hours before the start of the scan.

Snack options on the eve of an intensified tomography scan
If you are planning an MRI of any anatomical area with contrast, you should arrange a light snack 40-45 minutes before the procedure. This measure reduces the risk of autonomic reactions of the body to the contrast agent.
Progress of the procedure
It was said earlier that there is no need to prepare in any special way for the examination. Immediately before the scan, the patient receives instructions from a healthcare professional that you should remain calm and motionless until the end of the test. The patient is conveniently positioned on the equipment table, which subsequently slides into the device chamber.
The moving table stops its movement at the moment when the required area is in the field of action of the magnetic ring. If the patient suffers from claustrophobia, you can choose to study in an open-type apparatus; the choice of the option does not affect what the MRI of the lumbar region shows.
Recommendations before MRI
Additional measures apply to women during breastfeeding and children. The rule for preparing for an MRI for mothers planning to do a contrast-enhanced scan implies having a supply of expressed milk or formula for 2-3 times. After the administration of contrast, the baby should not be put to the breast for 6 hours.
Special preparation for MRI is needed if the examination is prescribed for a child. Babies are scanned in a hospital setting under general anesthesia, in the presence of an anesthesiologist. Children over 5 years old can already control their behavior, so you can do without medicated sleep.
It is important for parents to explain to their child that the procedure is absolutely safe and painless, and that mom or dad will be nearby. If necessary, someone close to you can accompany the child to the diagnostic room.
You can obtain detailed information about preparing for an MRI during an appointment at the Magnit DC. To quickly contact us, fill out the electronic form on the website or call +7 (812) 407-32-31.
Peculiarity
Speaking about how the MRI procedure of the lumbar region is carried out, it is worth saying that it is carried out strictly in two projections - sagittal and transverse. In addition, the device emits an unpleasant hum during operation, reminiscent of knocking or even buzzing. To make the scan as comfortable as possible, your healthcare professional may suggest using headphones that play pleasant, relaxing music. If the patient experiences severe pain, a painkiller is administered before the scan. If you are prescribed a tomography with contrast, you need to make sure that there is no allergic reaction to the substance.
Indications and contraindications for MRI
The study is prescribed to establish and clarify the diagnosis, postoperative monitoring and evaluate the results of therapy. Let us list the main indications for performing a magnetic resonance procedure.
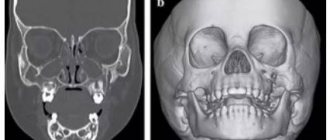
MRI of organs and structures of the head, facial skull, neck:
- changes in the hemispheres, midline and stem structures of the brain, accompanied by neurological disorders;
- neoplasms, metastases in the brain;
- tumors of the cranial nerves (for example, suspected neuroma);
- vascular diseases (ischemic lesions at any stage, malformations of arteries and veins);
- pathology of the pituitary gland;
- severe traumatic brain injury (diffuse axonal damage, contusion, cerebral edema, hemorrhage in the subacute and chronic phases);
- inflammatory diseases (meningitis, encephalitis, abscesses);
- demyelinating processes (multiple sclerosis, etc.);
- episyndrome and epilepsy;
- hydrocephalus;
- degenerative and metabolic pathologies;
- diseases of the paranasal sinuses;
- pathologies and eye damage (retinal detachment, tumors, inflammatory processes, hemorrhages on days 8-21);
- hearing diseases;
- changes in the pharynx and larynx;
- malignant and inflammatory lesions of the salivary glands;
- diseases of the neck area (thyroid and parathyroid glands, trachea, esophagus).
Schwannomas of both auditory nerves (indicated by white arrows) on MRI scans with contrast: on the left there is a giant tumor (inside the red circle)
MRI of the chest:
- breast tumors;
- neoplasms in the heart, lungs, adipose tissue and muscles;
- anomalies and pathologies of the aorta, veins, arteries, lymphatic system of the chest;
- emphysema, pneumonia (limited);
- some bronchial lesions;
- excessive amount of fluid in the pleural cavity and pericardium (if CT is contraindicated).
MRI of the spine:
- myelopathy;
- herniated intervertebral discs, including after surgery;
- pathologies of the cervical spine with cerebral symptoms or pyramidal disorders;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- spinal cord lesions of any origin;
- pathological conditions of nerve roots, ligaments, structures of the spinal canal;
- spinal cord neoplasms;
- spinal tumors;
- diseases of an inflammatory-dystrophic nature (spondylitis, including tuberculosis, etc.);
- multiple sclerosis;
- syringomyelia;
- multiple myeloma;
- spinal injuries in the presence of neurological symptoms.
Syringomyelia on an MRI scan (arrows indicate a cyst of the cervicothoracic spinal cord)
MRI of bones and joints:
- purulent osteomyelitis;
- aseptic necrosis;
- sacroiliitis;
- damage to the internal structures of the joints;
- bone tumor (if CT scan is not possible);
- functional disorders of the temporomandibular joint;
- pathologies of soft tissues of the musculoskeletal system.
Osteomyelitis of the calcaneus on MRI
MRI of the pelvic organs:
- inflammation, solid and cystic kidney formations;
- cancer of the ovaries, cervix and uterine body;
- endometriosis;
- ovarian cysts;
- inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system;
- prostate diseases (adenoma, cancer);
- bladder tumors;
- postoperative complications (fistulas, infiltrates, abscesses);
- pathologies of the rectum and sigmoid colon;
- inguinal hernia;
- congenital anomalies of organ development.
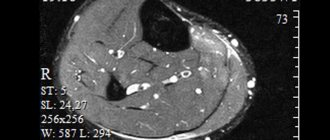
MRI of the abdominal organs:
- tumors and cystic formations of areas of interest;
- parasitic lesions (echinococcosis, alveococcosis, cysticercosis, etc.);
- organ malformations;
- inflammatory processes in the liver, pancreas, spleen, peritoneum, greater and lesser omentum;
- pathologies of large vessels;
- changes in retroperitoneal tissue (inflammation, destructive processes, damage to lymph nodes, etc.)
MRI scan of the abdomen
When MRI is contraindicated
MRI is prohibited if:
- pacemaker - the magnetic field can disrupt the operation of the device;
- electronic and ferromagnetic cochlear implants;
- endoprostheses;
- hemostatic clips of blood vessels;
- prosthetic heart valves installed before 1990;
- ferromagnetic fragments, surgical staples, pins, plates, etc.
Knee endoprosthesis
Relative contraindications to MRI:
- insulin pumps;
- neurostimulants;
- digital and analog hearing aids;
- prosthetic heart valves installed after 1990 for suspected dysfunction;
- decompensated heart failure;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- claustrophobia;
- serious condition or inappropriate behavior of the patient;
- drug, alcohol intoxication;
- presence of tattoos whose dyes contain metal (except titanium);
- body weight exceeding 120 kg.
Insulin pump
Contraindications for contrast studies:
- allergy to the components of the drug;
- pregnancy at any stage;
- severe renal and hepatic disorders.
How to dress for an MRI?
You can take the examination in your own clothes, if they are loose-fitting and do not restrict movement. The patient must take a horizontal position and remain motionless for about half an hour. Clothes should not press or dig into the skin. Try to choose cotton fabrics that are breathable.
In clothes that contain iron zippers and buttons, diagnostics with a tomograph cannot be carried out. You'll have to change into a medical gown.
When you go to the hospital, you should not wear jewelry, do complex hairstyles, or secure them with hairpins. You are not allowed to take gadgets into the MRI room.
Follow all the listed rules to obtain accurate data based on the results of the survey.
Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
What is the purpose of examining the spine with a tomograph?
Diagnostics using magnetic resonance imaging is carried out to assess the condition of the vertebrae. The doctor examines the spinal cord and cartilage, assesses the degree of blood circulation in the spine. This diagnosis is recommended for:
- Spinal column injuries;
- Chronic headaches;
- Curvature of the spine;
- Impaired motor coordination;
- Damage to the spinal column by infection;
- Presence of vertebral hernia.
MRI of the lumbosacral region is prescribed if other diagnostic methods are not informative enough. If the doctor does not have enough data to make an accurate diagnosis. This technique makes it possible to thoroughly analyze the location and condition of bones, assess their density, and diagnose tumors.