Pipelle endometrial biopsy refers to a diagnostic test that is performed using a disposable sterile catheter, which looks like a thin tube with an internal piston. This device was named the Peipel probe in honor of its creator. Thanks to this method, it has become possible to obtain a section of the endometrium in a minimally invasive way, without resorting to expansion of the cervical canal.
- Pros and cons of the study
- Indications and contraindications for pipell biopsy of the endometrium
- Research methodology
- After the procedure
- What the results show
- What complications are possible?
Advantages of the method
Pipelle biopsy is a more modern alternative to surgical endometrial biopsy.
Due to its low invasiveness, the procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis. The method by which it is performed does not require painful dilation of the cervical canal. Tissue aspiration is performed with a soft silicone probe with a diameter of about 3 mm. The probe has a hole at one end and a vacuum pump at the other. Despite the fact that the manipulation is a minor surgical procedure, the patient can leave the clinic within two hours after it. The main advantages of pipell biopsy of endometrial tissue include:
- possibility of carrying out on an outpatient basis;
- no need to dilate the cervix;
- minimum of discomfort;
- disposable probe, eliminating the risk of infection;
- low risk of complications after the procedure;
- short recovery period.
After the procedure
When the study is completed, the woman can immediately go home. During the first few days after a pipel biopsy, moderate nagging pain in the lower abdomen may be noted. As a rule, it does not cause significant discomfort and does not require painkillers.
Also, after the examination, slight bleeding from the genital tract may be observed. During this period, the woman is advised to abstain from sexual contact.
Another reaction of the body to endometrial aspiration biopsy may be a slight disruption of the menstrual cycle. Usually the delay does not exceed several days.
What is the procedure
Pipelle endometrial biopsy can be performed on an outpatient basis at any of the clinics in the Medoc network. On the eve of the study, the patient undergoes all the necessary tests, including a gynecological smear for infections and a series of blood tests. The day of manipulation is determined by the obstetrician-gynecologist based on the preliminary diagnosis and symptoms. The procedure is performed on a gynecological chair. To ensure minimal discomfort during the intervention, local anesthesia of the cervix is used. After the anesthesia has taken effect, a special pipell biopsy instrument is inserted into the organ cavity to aspirate endometrial samples. Using a probe, the doctor will suction out a small area of tissue for further examination. After one to two hours (if the condition is satisfactory), the patient can go home.
Pipel - biopsy of the endometrium of the uterus.
Pipelle biopsy is a minor gynecological operation that involves taking a part of the uterine mucosa using a thin disposable instrument (pipelle) and allows one to determine the condition of the endometrium (endometritis, LGE, polyposis, etc.). The operation is carried out after a preliminary examination in a surgical room under completely sterile conditions.
For the operation, it is necessary to donate blood for syphilis, HIV, hepatitis, a smear for vaginal microflora, a general blood test with platelets and clotting time, a general urine test, and ultrasound. The shelf life of the tests is 3-7 days.
The operation is contraindicated if :
- you have any acute infection,
- you have inflammation of the vagina (colpitis).
The operation is performed under local anesthesia, without dilating the cervical canal, using a pipel system. The operation is very gentle, almost painless, and is optimal for women planning a pregnancy. The resulting material is sent for histological examination to the laboratory, which makes it possible to subsequently choose the right treatment for you.
Preparation for surgery:
- Observe sexual rest for 3-5 days.
- Sanitize the vagina as recommended by your doctor.
- Shave your pubic hair 2-3 days before surgery.
- On the day of surgery, arrive at the clinic 15 minutes before the scheduled time.
- Warn your doctor about the tendency to bleeding, allergic reactions and seizures.
Need to know:
- There may be slight bleeding from the genital tract for 3-5 days after surgery.
- The next menstruation arrives at the expected time.
- It is recommended to monitor body temperature every evening for 5 days from the day of surgery.
- If your temperature rises above 37 degrees, severe pain, or heavy bleeding, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- All doctor’s recommendations must be strictly followed: for 3 days, observe sexual rest, do not douche, do not wash in the bathroom, do not take a steam bath, do not swim in open water, do not lift weights exceeding three kilograms, do not engage in physical exercise, avoid hypothermia and overheating. .
- On day 7, see your doctor.
- Be sure to find out the results of the pipel biopsy and receive recommendations for treatment.
Possible complications:
- Injury to the uterus , which is manifested by abdominal pain that can radiate to the collarbone, nausea, dizziness, and bleeding from the genital tract.
- Bleeding from the genital tract - copious, bright discharge, possibly with clots.
- Acute inflammation of the uterus , which can appear several hours or days after surgery and is manifested by high fever with chills, sharp pain in the lower abdomen, and general malaise.
In the event of a complication, the doctor undertakes to immediately admit the patient and provide her with free medical care, or refer her for inpatient treatment.
The price for this gynecological procedure in our price list is 2.33.1 Pipelle endometrial biopsy (without the cost of cytological / histological examination)
Indications for biopsy
Diagnostics may be recommended for the following diseases and conditions:
- too much menstrual flow;
- spotting outside of menstruation;
- cycle disorders;
- any endometrial neoplasms;
- infertility;
- miscarriage;
- adverse effects of hormonal therapy;
- bleeding during menopause;
- unsatisfactory condition after artificial termination of pregnancy (bleeding, pain, etc.);
- chronic endometritis;
- atrophic changes in the endometrium.
Technique for performing biopsy during hysteroscopy
Tissue sampling is performed using the CUG technique - a line-shaped scraping of the mucous layer is made from different parts of the uterus. A microsurgical curette is used. The total procedure time is up to 40 minutes.
Advantages of biopsy with hysteroscopy: compared to classical curettage and vacuum aspiration - non-traumatic, compared to pipette biopsy - much higher information content.
Mucosal samples obtained as a result of a biopsy are sent to the laboratory. Microscopic examination of tissues is carried out there. The analysis results are ready in 10-14 days. Taking them into account, the doctor plans further treatment tactics for the patient.
Nuances of preparation
Before a pipel biopsy of endometrial tissue, the gynecologist must make sure that there is no acute inflammatory process in the patient’s genitals. This requires taking gynecological smears for infections. You should also consult your doctor about taking blood thinning medications before the procedure. The full list of preparatory measures includes:
- consultation and examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- blood test for human immunodeficiency virus and syphilis;
- blood test for hepatitis B and C;
- clinical blood test;
- smear for genital infections;
- smear for cytology.
Sexual rest is required two to three days before the operation.
Material collection
In most cases, aspiration biopsy is performed on an outpatient basis without the use of anesthesia.
The Peipel catheter, which is used to collect biomaterial, is a thin (2-4 mm in diameter) plastic tube with a piston, which is then removed, causing fragments of endometrial tissue to be drawn inward.
After receiving the biomaterial, it is immediately sent for histological examination.
It usually takes about 1 minute to aspirate a piece of endometrial tissue.
When is a diagnostic procedure prescribed?
The study can be carried out for various diagnostic purposes. Let's consider for what pathologies and disorders it is necessary.
Infertility, failed IVF.
The condition of the endometrium plays a primary role in the onset of pregnancy. The process of successful implantation of the embryo in the uterus depends on the receptivity of the endometrium - structural and functional characteristics.
Depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, the structure and thickness of the endometrium changes. It reaches its greatest maturity during the implantation window, creating favorable conditions for fixation of the embryo in the uterus.
Taking a sample of the endometrium at the expected time of the implantation window and its further immunohistochemical study allows us to assess the receptivity of the endometrium, a decrease in which often leads to reproductive losses, the inability to get pregnant, and unsuccessful IVF programs.
In addition, a pipel biopsy is performed if there is suspicion of:
- anovulatory cycles, in which there is no ovulation and no phase of development of the corpus luteum;
- inflammatory and hyperplastic processes, which can be a source of infertility.
Bleeding of unknown origin, disruption of the menstrual cycle.
The study may be prescribed for bleeding of unknown origin: between menstruation, during menopause.
Also, the diagnostic procedure is performed for women with rare and frequent menstruation, changes in the volume of menstrual blood loss in the direction of increase/decrease. The indication for diagnosis is amenorrhea—the absence of menstruation for six months or more.
The cause of an unstable menstrual cycle and strange bleeding can be inflammatory and hyperplastic processes, endometriosis, and hormonal disorders. Pipelle biopsy of the endometrium allows you to accurately determine the cause of pathological symptoms.
Suspicion of endometrial cancer or other malignant processes in the uterus.
Endometrial cancer is one of the most common malignant diseases in women. Most often, pathology occurs during menopause. Histological analysis of a biopsy (material taken by biopsy) allows not only to detect a cancerous tumor, but also to determine the degree of its malignancy and sensitivity to hormone therapy.
Suspicion of endometriosis.
The disease is characterized by the penetration of cells of the inner layer of the uterus outside the organ. As a rule, the pathology occurs in women of reproductive age. There are many methods for diagnosing endometriosis, and pipel biopsy is one of them.
Endometrial polyps.
A polyp is a benign formation. However, any benign tumor under certain conditions can degenerate into malignant. For example, an adenomatous endometrial polyp is considered a precancer due to the fact that its cells are able to divide rapidly.
A biopsy is performed if differential diagnosis of a polyp is needed. Examination of the biopsy allows one to exclude the possibility of malignant degeneration of the tumor.
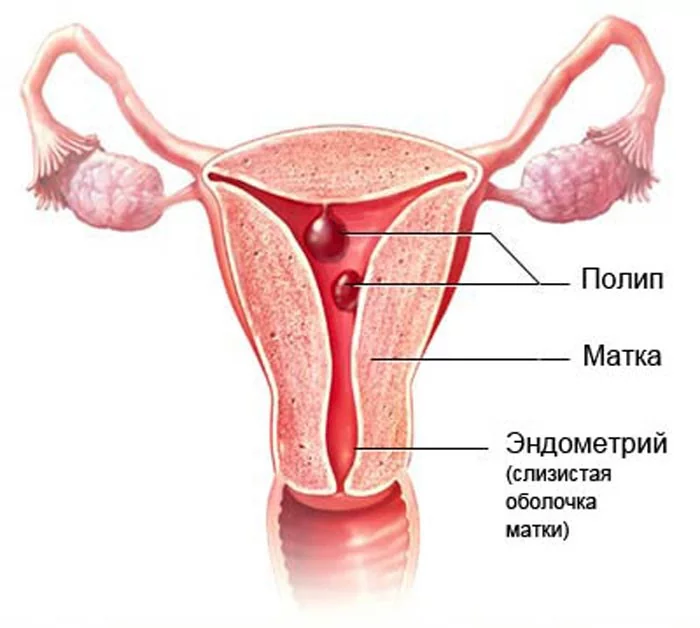
Suspicion of endometrial hyperplasia.
With pathology, thickening of the endometrium and certain changes in its structure are observed. You can suspect a problem during an ultrasound, but to make an accurate diagnosis, a core biopsy is required. In addition, the study allows us to understand whether it is atypical hyperplasia or not. Atypical hyperplasia is accompanied by changes in the structure and shape of cells and is a precancerous condition.
Suspicion of chronic endometritis.
The disease is an inflammatory process occurring in the endometrium. In the chronic form, the pathology leads to irregular menstruation, infertility, miscarriage and other consequences.
If endometritis is suspected, the biopsy specimen is analyzed for CD138 and CD56 markers, which appear in this pathology.
Monitoring the condition of the endometrium after surgical interventions.
Collection of endometrial elements may be necessary after curettage and other surgical interventions on the uterus. A biopsy allows you to evaluate how well the inner layer of the uterus has recovered after surgery.
Therapeutic and diagnostic hysteroscopy
- a hysteroscope is inserted into the woman through the external genitalia into the uterus through the cervical canal, with illumination and a video camera, which transmits to the monitor an enlarged image of the cervical canal and the internal cavity of the uterus, which allows the doctor to carefully examine the structure and (if present) pathology of the internal wall of the uterus, looking at them on the big screen.
Hysteroscopy is performed under intravenous anesthesia, which is painless and comfortable for patients.
Risk factors for developing endometrial hyperplasia
- hormonal disorders, namely, an excess of the hormone estrogen against the background of a deficiency of the hormone progesterone;
- concomitant diseases, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, diseases of the thyroid gland, mammary glands and adrenal glands;
- inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- abortions and diagnostic curettages;
- adenomyosis and uterine fibroids;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- hereditary disposition.
How to improve the endometrium before IVF
If the patient has not been diagnosed with pathologies of the uterine mucosa, her preparation for in vitro fertilization only includes taking hormonal drugs and auxiliary substances. Therapy is carried out in several stages:
- Estradiol preparations. This steroid hormone (estrogen) is produced by the follicular apparatus of the ovaries. It improves uterine circulation, increases the thickness of the endometrium, normalizes a woman's menstrual cycle, and stimulates the synthesis of other female sex hormones.
- Progesterone preparations. The purpose of this steroid hormone is to transfer the endometrium to the “secretory” stage, reduce the mother’s immune response to the embryo (which is half a foreign organism), and slow down the division of endometrial cells. Progesterone therapy is carried out both before and after IVF, to better secure the fertilized egg in the uterus.
In addition to hormonal therapy, in preparation for IVF, the patient is prescribed vitamin and mineral complexes containing B vitamins, vitamins A, E, C, zinc, iron, magnesium and other necessary elements. To correct the condition of the endometrium, the doctor also prescribes drugs that improve blood supply to the uterus.
Lifestyle in preparation for IVF
The patient’s nutrition plays an important role in preparing the uterus for in vitro fertilization. Food contains many substances that have a beneficial or, conversely, negative effect on the condition of the mucous membrane before IVF. Useful for building the endometrium are pineapple, raspberries, grapefruit, pumpkin, legumes, and vegetables. To prevent the mucous membrane from spreading to neighboring organs, it is recommended to eat beans, fish and poultry, and vegetables rich in fiber.
You also need to pay close attention to your lifestyle in general. Help to grow the endometrium before IVF:
- physical activity (just not excessive) - morning jogging, home fitness, Pilates;
- sound and regular sleep (at least 7 hours a day), lack of stress and anxiety;
- cessation of alcohol, smoking, and use of psychoactive substances, which has a systemic negative effect on the entire body.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
However, when using these “improvised” methods, remember that only a qualified doctor can provide truly high-quality and effective assistance in preparing for IVF. Taking medications, diet, activity level and other aspects must be previously agreed upon with him.
Why is it necessary to prepare the endometrium before IVF?
The endometrium is a hormone-dependent tissue, whose thickness, cellular composition and other characteristics change over time (during the menstrual cycle) under the influence of sex hormones. In vitro fertilization, in turn, is not a physiological norm for a woman’s body. This is a completely artificial and human-controlled procedure, the purpose of which is to implant a fertilized egg into the uterus with the highest probability of success. Accordingly, these two factors need to be brought into line with each other.
For a successful pregnancy, the endometrium must have fairly strict characteristics:
- Thickness – 9-11 mm;
- High concentration of blood vessels;
- A large number of secretory cells.
Any deviation from these parameters, even minor, significantly reduces the likelihood of a successful pregnancy. Therefore, before embryo transfer, the doctor studies the characteristics of the endometrium. Its thickness is of greatest importance - if on an ultrasound examination it is more or less than the specified norm, then the procedure is canceled. The situation is more complicated with the blood supply and cellular composition of the mucosa, which can only be studied with the help of a biopsy.
Complications of hyperplasia
In the absence of proper and adequate treatment, endometrial hyperplasia leads to severe anemia with a significant decrease in hemoglobin levels, weakness, increased fatigue, and drowsiness, which is associated with large blood losses during menstruation. In young women, endometrial hyperplasia can cause infertility and miscarriage. Certain forms of endometrial hyperplasia (glandular and cystic endometrial hyperplasia) are a precancerous condition and, in case of long-term observation, in the absence of treatment, can degenerate into uterine cancer.
Preventive measures for this disease are necessary in order to reduce the risk of developing endometrial cancer and prevent recurrence of hyperplasia.
- 1. Timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs before they become chronic.
- 2. If there is a diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia, follow-up with a gynecologist 2 times a year for 3 years.
- 3. Annual examination by a gynecologist, pelvic ultrasound for all women, regardless of age.
- 4. Observation by a general practitioner. an endocrinologist in the presence of risk factors for the development of endometrial hyperplasia.
- 5. Regular physical activity, following a diet low in easily digestible carbohydrates.
Causes of endometrial disease
Most often, endometrial diseases are caused by the following reasons:
- Inflammatory process (endometritis) - can be caused by bacterial, viral, parasitic, fungal, mycoplasma, protozoal and other infections and is often chronic. Treatment of chronic endometritis before IVF should be carried out in advance;
- Hormonal disorders - hyperplasia (excessive growth) of the endometrium or polyps (focal growths) of the endometrium;
- Endometrial trauma - during curettage of the uterine cavity can lead to the formation of intrauterine adhesions or atrophic processes.
Endometrial pathologies can lead to disturbances in the menstrual cycle, the process of embryo implantation, spontaneous abortions, the formation of placental insufficiency, and infertility.
Timely diagnosis of endometrial diseases is necessary in the comprehensive diagnosis of menstrual disorders, reproductive problems and infertility treatment.