Pulmonologist
Prokhina
Maria Egorovna
Experience 38 years
Pulmonologist
Make an appointment
The pathological process of proliferation of fibrous (connective or scar) tissue in the lungs with its gradual replacement of pulmonary alveolar tissue is called fibrosis. The process is characterized by a gradual decrease in respiratory function up to a critical level. The tissue that forms the lungs becomes less and less elastic and stretchable. The compaction complicates gas exchange: it becomes more difficult for oxygen and carbon dioxide to penetrate the walls of the alveoli, and the ability of the lungs to expand is gradually lost. Depending on the localization of the formation of fibrous areas and the reasons for their appearance, the general course of the disease depends.
Why does scar tissue grow?
Often the cause of pulmonary fibrosis is a disease that affects the lung tissue:
- infectious inflammatory process (pneumonia of any origin, cytomegalovirus infection, tuberculosis, syphilis, etc.);
- chronic obstructive inflammatory disease (bronchial asthma, etc.);
- an occupational disease associated with dust particles or aggressive gas entering the lungs;
- pulmonary sarcoidosis;
- allergic lung disease associated with inhalation of air containing antigen particles;
- vasculitis - inflammation of the wall of the pulmonary vessels;
- systemic autoimmune disease;
- recovery of the body after surgery on the lungs, which occurs with excessive formation of fibrous tissue;
- disease of another internal organ or body system associated with the formation of scar tissue;
- radiation therapy performed to treat cancer;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- chronic cytomegalovirus infection.
In cases where it is not possible to determine the disease that caused the growth of connective tissue in the lungs, doctors talk about idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Strengthening the pulmonary (vascular) pattern
The pulmonary pattern is a normal component of fluorography. It is formed largely by the shadows of blood vessels: arteries and veins of the lungs. This is why some use the term vascular (rather than pulmonary) pattern. Most often, an increase in the pulmonary pattern is observed on the fluorogram. This occurs due to more intense blood supply to the lung area. An increase in the pulmonary pattern is observed in acute inflammation of any origin, since inflammation can be observed both in banal bronchitis and in pneumonitis (cancer stage), when the disease does not yet have any characteristic signs. That is why in case of pneumonia, which is very similar to pneumonitis in cancer, a repeat image is required. This is not only control of treatment, but also the exclusion of cancer.
In addition to banal inflammation, an increase in the pulmonary pattern is observed in congenital heart defects with enrichment of the small circle, heart failure, and mitral stenosis. But these diseases are unlikely to be an incidental finding in the absence of symptoms. Thus, increased pulmonary pattern is a nonspecific sign, and in cases of ARVI, bronchitis, pneumonia, it should not cause any particular concern. Increased pulmonary pattern in inflammatory diseases, as a rule, disappears within a few weeks after the illness.
How to recognize the disease
At an early stage, the process of replacing lung tissue with scar formations is almost impossible to notice, since this process is asymptomatic and does not cause discomfort to the patient until a certain point. Characteristic symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis appear after the process covers a significant part of the lungs, due to which a decrease in respiratory function becomes noticeable, expressed in:
- shortness of breath, which initially occurs only after increased physical activity and gradually becomes chronic;
- cough, which at the initial stage occurs rarely and remains dry, and then becomes more frequent, and sputum production is added to it;
- bursting pain in the chest, which occurs due to impaired elasticity of the lungs and an increase in their volume;
- cyanosis (blueness of the skin) due to a chronic lack of oxygen in the tissues;
- the appearance of characteristic thickenings on the last phalanges of the fingers and changes in the shape of the nail plates;
- fatigue associated with insufficient oxygen supply to tissues;
- problems with the activity of the heart and blood vessels due to a lack of oxygen entering the heart muscle.
The listed signs may also indicate other, no less serious diseases, so if they appear, you should consult a doctor and get your condition examined.
Are you experiencing symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Sinus free or sealed
Pleural sinuses are cavities formed by folds of the pleura. As a rule, in a full description of the image, the condition of the sinuses is also indicated. Normally, they are free. In some conditions, effusion (fluid accumulation in the sinuses) may occur, and its presence clearly requires attention. If the description indicates that the sinus is sealed, then we are talking about the presence of adhesions, which we discussed above. Most often, a sealed sinus is a consequence of previous pleurisy, trauma, etc. In the absence of other symptoms, the condition is not cause for concern.
Diagnostic methods
To identify pulmonary fibrosis, the doctor prescribes a number of tests:
- fluorography as a screening method for quickly identifying the disease;
- X-ray of the lungs to clarify the diagnosis;
- high-resolution computed tomography to clarify the prevalence of fibrous changes, the nature and dynamics of the process;
- laboratory blood test for oxygen and carbon dioxide levels;
- oximetry to determine the amount of oxygen in arterial blood;
- spirometry and determination of the diffusion capacity of the patient’s lungs;
- six-minute walk test to determine changes that occur in the body during physical activity.
If necessary, a biopsy of lung tissue may be performed.
Norms
Normally, structural pathology is not visualized in the examined organs.
Fluorography of the lungs is the study of the chest organs using X-rays that penetrate the lung tissue and transfer the pattern of the lungs onto film through fluorescent microscopic particles.
A similar study is carried out on persons over 18 years of age. The frequency of this is no more than once a year. This rule applies only to fluorography of healthy lungs, when further examination is not required.
Modern methods of treatment
Currently, there are no methods for treating pulmonary fibrosis that would lead to the restoration of lung tissue in full or even partial volume. The doctor’s task is to determine the cause of the proliferation of connective tissue and stop this process. Some progress in this direction has already been achieved. In cases where fibrosis is a consequence of an inflammatory or autoimmune process, therapy eliminates the inflammatory process and the proliferation of fibrous tissue stops.
In general, treatment for fibrosis includes:
- stopping the action of factors that provoke the growth of scar tissue - changing the type of activity or workplace to eliminate the harmful effects of dust;
- treatment of infectious or autoimmune pulmonary disease;
- suppression of fibrous growths with the help of special medications - glucocorticoids and cytostatics;
- regular breathing exercises to improve respiratory function;
- oxygen replacement therapy in a medical facility or at home.
If the lung tissue is severely damaged, the patient at a young age is prescribed a lung transplant or surgical removal of the focus of fibrous tissue growth.
There is no need for special nutrition for pulmonary fibrosis. The patient's diet should be healthy and varied, preferably with a high content of protein products. It is recommended to divide the daily amount of food into small portions consumed at short intervals. Smoking, including passive smoking, is strictly prohibited. The patient needs to avoid stress and learn techniques that improve respiratory function.
Darkening in the picture is not necessarily a pathology
Darkening in the picture does not necessarily mean oncology or tuberculosis, although this, of course, can also indicate a serious pathology. In addition, an eclipse may appear in the image when smoking cigarettes for a long time (see What does fluorography of a smoker’s lungs show: are changes visible?).
Hence, it is difficult to immediately determine what darkening in the right or left lung may mean on fluorography. Maybe a foreign object got there?
This often happens with curious children. Note that the types of eclipses are not directly related to pathologies, and the problem cannot be immediately determined by the shape of the spot.
A dark spot on the lung on fluorography is divided by number and size. Single spots indicate tumors; they can be malignant or benign.
If there is more than one darkening in the lungs on fluorography, then this indicates the presence of several pathologies. The location of the spots is also important.
So, if a darkening in the lungs on fluorography shows damage to the apex of the organ, then this may indicate tuberculosis, but the doctor must prescribe, in addition to tests, a repeat image.
FAQ
How dangerous is pulmonary fibrosis for humans?
The proliferation of fibrous tissue leads to a decrease in the working volume of the lungs and a decrease in the amount of air entering the body when inhaling. A person lacks oxygen, he begins to choke when walking, and subsequently in a calm state. Pulmonary insufficiency leads to the development of pulmonary hypertension, emphysema, bleeding, pneumothorax, and lung rupture. The risk of degeneration of lung tissue into a malignant tumor increases significantly.
How to stop pulmonary fibrosis with folk remedies?
Traditional medicine recipes in many cases perfectly complement the main course of treatment for fibrosis, but they can only be used after consultation with your doctor. Among the most popular remedies are a decoction of anise seeds (a tablespoon of seeds is poured into a glass of boiling water) and tea made from a mixture of crushed rose hips and elecampane root.
How do you know if you have pulmonary fibrosis?
If you constantly feel shortness of breath, lack of air and chest discomfort, you should contact a pulmonologist (a doctor who specializes in the treatment of lung diseases) or your primary care physician, who will refer you to a specialist for consultation. Fibrosis can be diagnosed only after an X-ray examination.
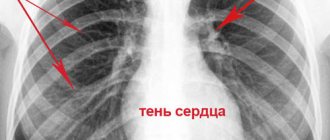
The mediastinal shadow is widened/displaced
Particular attention is paid to the shadow of the mediastinum. The mediastinum is the space between the lungs. The organs of the mediastinum include the heart, aorta, trachea, esophagus, thymus, lymph nodes and vessels. The expansion of the mediastinal shadow, as a rule, occurs due to an enlargement of the heart. This expansion is most often unilateral, which is determined by an increase in the left or right parts of the heart.
It is important to remember that according to fluorography, you should never seriously assess the condition of the heart. The normal position of the heart can fluctuate significantly, depending on the person’s physique. Therefore, what appears to be a shift of the heart to the left on fluorography may be the norm for a short, overweight person. Conversely, a vertical or even “teardrop-shaped” heart is a possible normal option for a tall, thin person.
In the presence of hypertension, in most cases, the description of the fluorogram will read “mediastinal widening to the left,” “heart widening to the left,” or simply “widening.” Less commonly, uniform widening of the mediastinum is observed, indicating the possible presence of myocarditis, heart failure, or other diseases. But it is worth emphasizing that these conclusions do not have significant diagnostic value for cardiologists.
A shift of the mediastinum on a fluorogram is observed with an increase in pressure on one side. Most often this is observed with an asymmetric accumulation of fluid or air in the pleural cavity, with large tumors in the lung tissue. This condition requires the fastest possible correction, since the heart is very sensitive to gross displacements, that is, in this case, an urgent visit to a specialist is necessary.