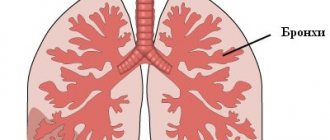
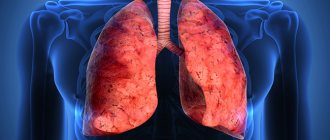
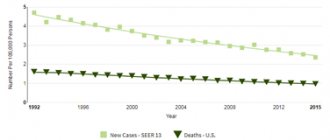
Breathing is a process without which a person cannot exist. Anyone who cares about their health should know where a person’s lungs are, how they function and what structure they have. The organ is vital because it supplies the entire body with oxygen.
Common ailments
As mentioned below, regular smoking leads primarily to changes in the structure of the organs of the respiratory system. These changes in morphology contribute to the development of a number of diseases. Among them, the most common when smoking are:
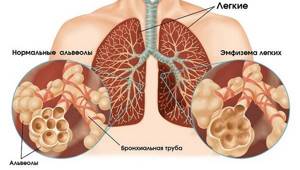
- Emphysema. The lungs of a person with emphysema due to smoking do not change specifically, so we can only assume that he smokes. What is emphysema? The disease is a consequence of changes in the structure of the pulmonary alveoli. Normally, the alveoli, which are the final structure of the lungs of any person, are small in size, each of them is surrounded by a special septum. The main function of the alveoli is gas exchange.
Smoking negatively affects the alveoli themselves. The harmful substances contained in tobacco smoke contribute to the occurrence of an inflammatory process, leading to the destruction of the alveolar septa. Small alveoli unite with each other into large cavities, and sometimes huge air sacs. As a result, changes are visible on x-rays. An X-ray of the lungs of a smoker with emphysema has a very characteristic picture: the organs resemble bags or honeycombs, visible as clearing against the background of a darker pattern of unchanged tissue or lung tissue with fibrosis. At this stage, even if a person stops smoking, the pulmonary pattern will not change. The chest x-ray of a heavy smoker with emphysema will remain unchanged for the rest of his life.
- Chronical bronchitis. The mechanism for the formation of changes in the lungs of a smoker is similar to the previous one. As a result of exposure to cigarette smoke, an inflammatory process occurs in the respiratory tract, leading to the formation of a large amount of viscous mucus. It blocks the normal outflow of mucus from the lungs and is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. The processes lead to disruption of gas exchange. Compensatory lung expansion and deformation occurs in a smoker. In the early stages of chronic bronchitis, the lungs of a heavy smoker and a healthy person cannot be distinguished by X-ray. This stage is favorable for quitting smoking and giving up cigarettes forever. Continued smoking of cigarettes will lead to irreversible changes.
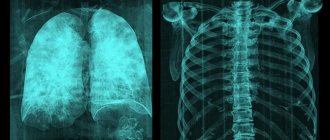
Photo of an x-ray of a healthy person and a smoker:
Healthy lungs have a large compensatory reserve of their own capabilities. A person starts smoking cigarettes and for a long time does not feel any significant changes in his own health, especially if the smoker is at a young age. Only after a few years do the first characteristic changes appear, and they may not appear immediately and the symptoms may be nonspecific. People who start smoking are more likely to suffer from colds over time, and the illnesses can have a protracted course and require the prescription of antibiotics.
Everything is complicated by the fact that a person who continues to actively smoke cigarettes does not see external changes. He looks healthy. The changes first appear clinically in the form of the symptoms described above, only then become visible during a computed tomography scan, which is not a routine examination and is not performed frequently. Only after five or even more years do the characteristic lungs of a smoker appear on X-ray.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Iron deficiency
Allergy
COVID-19
8843 09 April
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Synonyms: Chronic obstructive bronchitis, emphysema, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive, life-threatening lung disease characterized by inflammation of the airways and obstruction (swelling) of the bronchi. This disease is not always easy to diagnose, which increases its danger.
The criterion for COPD is chronic inflammation that affects the central airways, peripheral airways, lung parenchyma, alveoli and pulmonary vasculature.
COPD includes:
- Chronic obstructive bronchitis, in which the patient has a wet (productive) cough for three months or more, not caused by other diseases.
- Emphysema is a pathological expansion of internal cavities (in this case, the lungs), in which tissues stretch and swell unnaturally. A so-called valve mechanism arises - air easily penetrates into the tissue, but comes out with difficulty. Obliteration of the small airways is thought to be the primary injury preceding the development of emphysema.
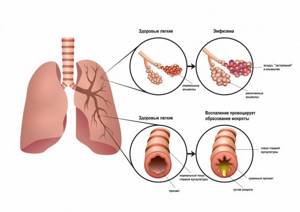
Enlarged alveolar spaces sometimes aggregate into bullae (air cysts), defined as air spaces ≥ 1 cm in diameter. These changes lead to a loss of elasticity of the lung tissue and the development of hyperairiness. Causes of COPD
The main cause of COPD is airflow limitation caused by an inflammatory response to inhaled toxins, most commonly tobacco smoke, including secondhand smoke.
Other reasons for the development of the disease include unfavorable environmental conditions (air pollution from industrial waste, exhaust gases, smoke, dust, etc.), professional activity (work in mines, chemical plants, hot shops), climatic conditions (high air humidity ), infectious agents (mycoplasmas, pneumococci, Haemophilus influenzae, influenza viruses, adenoviruses, etc.).
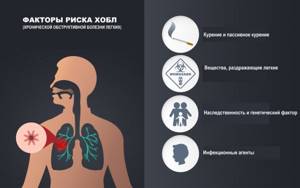
Risk factors for the development of COPD include alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, high levels of immunoglobulin IgE, family history of the disease, genetic predisposition (blood type A (II), absence of IgA).
COPD takes years to develop. Typically, the first symptom is a productive cough, which develops in smokers aged 40–50 years. Most patients smoke more than 20 cigarettes/day for more than 20 years. Exacerbations and comorbid conditions are an integral part of the disease and make a significant contribution to the clinical picture and prognosis. As COPD progresses, exacerbations of the disease become more frequent, averaging 1-3 episodes per year. Since COPD is a progressive disease, complete normalization of lung function is not possible.
Classification of the disease
International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (J44):
J44.0 – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with acute respiratory infection of the lower respiratory tract.
J44.1 – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with exacerbation, unspecified.
J44.8 – Other specified chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chronic bronchitis: asthmatic (obstructive), emphysematous.
J44.9 – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, unspecified.
In 2011, a classification
, developed by the international group of GOLD experts and based on an integral assessment of the severity of COPD:
A – low risk of exacerbations, symptoms are not expressed; B – low risk of exacerbations, symptoms are severe; C – high risk of exacerbations, symptoms are not expressed; D – high risk of exacerbations, symptoms are severe.
Symptoms of COPD
The main symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease include:
- shortness of breath, or a feeling of lack of air - initially during physical activity, subsequently at rest; shortness of breath increases in a dusty environment, in the cold, in the presence of irritating substances in the air;
- chronic cough with or without phlegm;
- prolongation of the expiratory phase during quiet and especially during forced breathing;
- wheezing;
- barrel-shaped chest (anterior-posterior size of the chest increases).
The progression of COPD is manifested by an increase in cough and an increase in the amount of sputum, which can be purulent.
In the future, difficulty breathing occurs even when performing simple actions - walking or getting dressed. At the same time, patients begin to lose weight, feel inexplicable weakness, they develop cyanosis (blueness) of the skin, signs of heart failure increase, swelling of the legs occurs, fluid may accumulate in the abdominal cavity (ascites), and the liver enlarges. Exacerbations can lead to a marked decrease in work ability and the need for emergency medical care (including hospitalization).
Diagnosis of COPD The disease can be suspected based on history, physical examination and x-ray examination. The diagnosis is confirmed by functional breathing tests. The most important diagnostic method is spirometry, where the vital capacity of the lungs, forced expiratory volume in 1 second and other indicators are measured according to a certain scheme.
What will the photo show?
Fluorography of a smoker's lungs does not have specific changes indicating that it was smoking that led to them. Signs of this kind can develop in healthy people when working in hazardous industries, be a consequence of unfavorable ecology (air pollution), or be a symptom of a disease. However, if this kind of influence is excluded, and a healthy person continues to smoke for a long time, we can say with some confidence that the doctor is seeing fluorography of a smoker.
What do smoker's lungs look like? First of all, the lungs of a healthy person and the lungs of a chronic smoker are distinguished by the presence of a thickened pulmonary pattern on x-ray. This happens due to the proliferation of connective tissue in the most distant parts, that is, in the alveoli, or rather, the “sacs” surrounding them. At the same time, thickening of the small bronchi occurs, which, against the background of mucus stagnation, causes the alveoli themselves to expand - bronchiectasis is formed. Now we will describe in more detail how a normal x-ray differs from an x-ray of the lungs of a smoking patient. This is not difficult to do:
- Normally, the lungs are visible in the form of transparent fields; against the background of the darker lung tissue, the light contours of the bronchi and vessels will be visible, especially clearly visible at the root of the lung. Peripheral, that is, small bronchi are not normally visible on x-rays. In a person who smokes a cigarette, connective tissue grows, which will cause a thickening of the pulmonary pattern. The thickening of the pattern is determined by counting the number of small shadows in one segment formed by the intersection of the shadows of the ribs.
- Clearing of the pulmonary fields in the periphery. Occurs simultaneously with the changes described above. Clearing along the outer contour of the lung in a smoker is a consequence of the lungs’ attempt to “adapt” to the smoker’s lifestyle and stabilize gas exchange.
Characteristic signs of smoking can also form in the area of the roots of the lungs, that is, the part where the two large main bronchi end and the lung tissue itself begins. An X-ray of a smoker may reveal a lack of structure in the roots, the presence of additional shadows, blurred and indistinct contours, deformation of the pattern and an increase in tissue density. Now let's explain in more detail what each term means.
Photo of a smoker's black lungs:

Poor structure in a smoker is characterized by the inability to clearly identify the structural elements of the bronchopulmonary system: to determine the head, body, and tail of the lungs. Blurred contours in a smoker mean the absence of clear outlines of the bronchi due to the proliferation of connective tissue. Deformation of the roots is caused by inflammatory processes: the roots lose their even, clear, straight outlines, and the course of the bronchi becomes tortuous on the x-ray of a smoker. Radiologists call this symptom the X-ray symptom of low structure.
Primary and secondary functions
The main function of the lungs is the exchange of gases between the blood and the atmosphere. But there are many more secondary functions:
- Change blood pH;
- Under the influence of angiotensin-converting enzyme, angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II;
- Serve as protection for the heart, protecting it from shock;
- They release antimicrobial compounds and immunoglobulin-A into bronchial secretions, thereby protecting the body from various respiratory infections. Bronchial mucus contains glycoproteins with antimicrobial effects, such as lactoferrin, mucin, lactoperoxidase, lysozyme.
- The lungs serve as a kind of blood reservoir in the human body. The blood volume in this respiratory organ is approximately 450 milliliters, which is approximately 9% of the total blood volume in the circulatory system.
- Providing airflow is required to create vocal sounds.
- The ciliated epithelium of the bronchi is a very important defense system against various infections that are transmitted by airborne droplets.
- Due to the evaporation of water from the alveoli into the exhaled air, thermoregulation occurs.
Visible changes
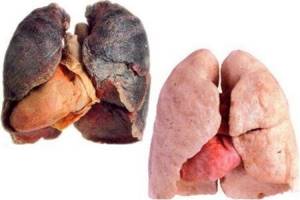
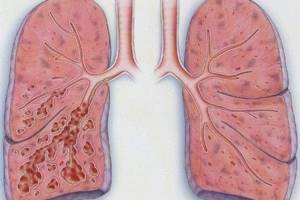
The lungs of a smoker and a healthy person are very different in appearance - pathologists immediately see the difference during an autopsy. In normal condition, the lungs are pink. In people with nicotine addiction, they are black, with a soot residue.
The difference between what a smoker's lungs look like and an organ that has not been harmed is not just a matter of color. In people with an addiction, it has a number of specific features:
- the originality of the design, which is characterized by a large number of exfoliated elements;
- lymph nodes are noticeably enlarged due to the accumulation of lymph fluid, calcite, and dirt;
- deformation of the root region of the lungs is observed due to the active proliferation of connective tissue;
- there are multiple cavity formations - in appearance the organ resembles a sieve;
- the root part of a healthy person is straight, while in a smoker it is curved;
- Light areas are observed in the lower part of the lungs - an indication of pulmonary insufficiency.
The changes that occur can be detected not only after autopsy, they are noticeable on an x-ray. Fluorography can detect changes only in cases of cancer or tuberculosis.
Nose organ of smell
The nose is able to distinguish the smells of the surrounding world (Fig. 12).
Rice. 12. Nose is the organ of smell (Source)
This is the organ of smell . The first smell that a person encounters is the smell of mother's milk. The sense of smell is primarily needed to test the suitability of food and air. If food has spoiled, you can easily feel it and will not eat it (Fig. 13).
Rice. 13. The sense of smell helps determine the suitability of food (Source)
Thus, the sense of smell saves our lives. Molecules of odorous substances, along with the flow of inhaled air, enter the nasal cavity. Here, in the upper part, there is a special olfactory surface . It is small in size, its area is no more than three square centimeters. This is approximately the size of a small postage stamp. This small surface contains more than two hundred million special cells. Each such cell is covered with mucus and has a special outgrowth (Fig. 14).
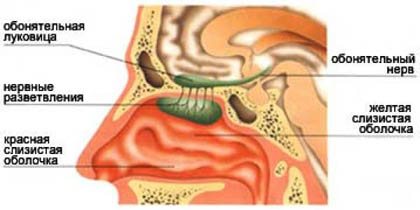
Rice. 14. Olfactory system (Source)
It is in mucus that molecules of odorous substances dissolve. The signal travels through special nerves to the brain, and you and I distinguish between smells. Thus, the nose is a unique mechanism capable of distinguishing odors, an important organ of the respiratory system .
Lung diseases associated with smoking
Exposure to nicotine changes the structure of the organ, which leads to the development of the following diseases:
- Emphysema. With pathology, the structure of the alveoli changes. As a result of smoking, an inflammatory process begins, which leads to the destruction of the partitions between the alveoli. Small alveoli connect to form cavities. These areas are easy to spot on an x-ray because they are lighter in color compared to healthy (darker) areas.
- Chronic form of bronchitis. The pathogenesis of the disease is similar to the previous one: the root cause is an inflammatory process, which leads to the production of a large amount of a viscous substance that blocks the normal discharge of functional lung mucus. The resulting environment is ideal soil for the growth of bacteria. As a result, gas exchange is disrupted. People who smoke experience compensatory enlargement of the lungs and their deformation. Even an x-ray cannot detect the initial stage of chronic bronchitis.
- Pneumonia is also a consequence of inflammation of the lung tissue. Irritation of the mucous membranes of the alveoli stimulates the release of exudate, which, combining with nicotine and tar, fills the lower alveoli. Progression of the process leads to their atrophy, reduction in expiratory volume, and development of pulmonary failure.
- Characteristic symptoms are: sputum production, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue.
- Smoking is also one of the causes of lung cancer. At the initial stage, oncology is detected only by chance - during a medical examination. There are no specific signs of a fatal disease during this period. Later, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, chest pain, and hemoptysis appear.
- The risk of tuberculosis increases significantly. It is important to know that irregular smoking of cigarettes leads to changes in the radiograph.
Larynx, epiglottis
From the nasal cavity , bypassing the nasopharynx , air enters the larynx (Fig. 15) .
Rice. 15. Larynx(Source)
If you touch the person's neck in front, you can feel the ribbed, hard surface of the larynx. Here the sounds of the voice are born: in the larynx there is a special glottis in which the vocal cords (Fig. 16), when we exhale (and it is when we exhale that we pronounce sounds), the vocal cords begin to vibrate, like the strings on a musical instrument, we make sounds.
Rice. 16. Vocal cords(Source)
The larynx is also lined from the inside with a mucous membrane, which is a barrier to bacteria and other harmful substances. The larynx is where the respiratory and digestive systems intersect. But food must enter the esophagus, and air must enter the respiratory tract. To ensure that food and air move in the direction they need and not mix, nature created a unique valve mechanism, which was called the epiglottis (Fig. 17).
Rice. 17. 1 epiglottis; 2 food; 3 larynx. (Source)
It hangs like a guard over the entrance to the larynx and closes every time food or liquid enters the oral cavity, so we can eat and breathe at the same time.
How does organ destruction occur?
The lungs of a smoker and a non-smoker differ in functionality. In a healthy state, they can independently clean their surface from dust penetrating inside. Thanks to the ciliated epithelium, particles of contaminants are promoted and removed through coughing. This applies to common substances that we encounter every day. In the case of smoking, the situation is much more complicated.
Tobacco smoke contains tars and combustion products. When this combination penetrates the respiratory system, the cilia of the epithelium are damaged, they stick together and can no longer perform the cleansing function.
As a result, the incoming soot settles in the lower part of the lungs. As already mentioned, the formation of cavities is observed, and in which dirt accumulates even faster.
Respiratory system and human voice
One of the elements of the human respiratory system, the trachea in its upper part passes into the larynx (we can say, on the contrary, that the larynx in its lower part passes into the trachea). Inside the larynx there are two folds called the vocal cords. Normally the vocal cords are open, but if they are compressed, the air passing through the larynx during exhalation will cause them to vibrate, and it is as a result of the vibration of the vocal cords that the sounds of a person's voice are created. A person can change their voice by changing the pressure of exhaled air on the vocal cords or changing their shape.
Harm of electronic cigarettes to the lungs
Smoking a vape in no way reduces the harm it causes to the body. American scientists conducted a study that assessed the changes that occur in cells after inhaling liquid. Regardless of whether it contained nicotine, negative effects were observed.
The longer the inhaled vapor remained in the lungs, the more serious violations were recorded. Firstly, it also contains carcinogens. Secondly, its particles are smaller and therefore are able to penetrate into the very depths of the organ. You should not think that electronic cigarettes are safer - this is a myth, because in them natural nicotine is replaced with chemical one, which is even more harmful.
An interesting comparison is the effects of cigarette smoke and marijuana smoke. Despite the fact that their composition is almost identical (apart from the presence of cannabinoids), scientists believe that the harm to the lungs is less. This is explained by the fact that marijuana is smoked less often, and in general the condition of the lungs is affected by the total amount of inhaled toxins.

It is impossible not to touch upon such a “fashionable” topic as hookah smoking. Compared to tobacco, fewer harmful substances will enter the body. However, it is also dangerous for the lungs. 10-15 years of hookah smoking leads to the death of the alveoli in the same way as in the case of cigarettes.
How does oxygen get into the blood?
Through the thin walls of the alveoli, oxygen enters the blood vessels. Here it is picked up by “transport” - hemoglobin
, which is contained in red blood cells. At the same time, carbon dioxide enters the opposite direction - into the alveoli - from the blood, which is removed from the body when exhaling. Oxygenated blood is sent from the lungs to the left side of the heart, from where it is distributed throughout the body through arteries. As soon as the oxygen in the blood is used up, the blood flows through the veins to the right side of the heart and from there back to the lungs.
Passive smoking
It is necessary not only to give up the bad habit, but also to protect yourself from tobacco smoke in principle. Even with passive smoking, the same carcinogenic substances enter the body, because only part of them settles in the smoker’s lungs.
It is a provoking factor for the following pathologies:
- bronchial asthma;
- cancer diseases;
- inflammation of the respiratory system, hearing organs;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
Under the influence of tobacco smoke, sleep and appetite are disturbed, the nervous system is weakened, and emotional lability is observed.
Oncological causes
The cause of pulmonary edema or hydrothorax in cancer patients can be both the cancer itself and its treatment.
For example, fluid accumulation and pulmonary edema can occur as a result of chemotherapy with toxic drugs that depress the heart, or as a complication of radiation therapy. On the other hand, the functioning of the heart can be disrupted by the tumor process.
Another possible reason is disruption of the lymphatic system due to damage to the lymph nodes by metastases or germination of a cancerous tumor.
Most often, fluid accumulation occurs in cancer of the lung, breast, ovary, stomach, body and cervix, melanoma, lymphoma, sarcoma, and leukemia.
With a malignant tumor of the pleura (mesothelioma), the permeability of the vascular wall of the capillaries increases. Fluid from the blood actively enters the lungs, and its pumping by the lymphatic system, on the contrary, worsens. As a result, stagnation and fluid accumulation occurs.
Other reasons are also possible, for example, compression of the heart by a tumor, tumor growth into the superior vena cava, formation of metastasis in the pericardium, tumor growth into the lumen of the bronchus and its overlap.
Oncological diseases are characterized by a gradual, slow development of hydrothorax and pulmonary edema.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Lung cleansing
When a person realizes that it is time to stop burning his lungs, the question of restoring their functionality arises. A prerequisite on the path to restoring the respiratory system is giving up cigarettes and avoiding passive smoking. For most people, eliminating the habit from life is accompanied by coughing attacks. This can be considered normal, since the body begins to remove accumulated tars and impurities, while during smoking, nicotine suppresses the cough reflex.

If a person is seriously thinking about how to return the lungs to their previous state, experts recommend changing the situation and moving for a while to an ecologically clean area. If this is not possible, you should spend more time outdoors - in parks, squares, and walks in the forest.
It is necessary to increase physical activity. Sports activities will help improve blood circulation, and therefore the delivery of oxygen to organs and tissues. It is recommended to walk, ride a bike, or jog. The duration of classes must be at least 25 minutes. If there is a deterioration in health, shortness of breath, tachycardia, then the intensity of training must be reduced.
Homemade inhalations with herbal decoctions will help cleanse your lungs after smoking. You can use oak bark, sage, chamomile. Inhalation may be accompanied by an increase in the cough reflex; this is normal.
Cleansing with herbs can be carried out not only through inhalation, but also by taking decoctions orally. It is recommended to drink teas with thyme, pine buds, and plantain. They are drunk several times during the day between meals.
Special breathing exercises from yoga and bodyflex will stimulate renewal processes in the bronchi and activate the removal of contaminants from phlegm. As they are completed, the immune system is strengthened and heart and vascular diseases are prevented.
The diet also helps cleanse the lungs. It is necessary to consume dairy products, garlic, onions, fruits and vegetables.
It is recommended to regularly visit the bathhouse or sauna - profuse sweating will help remove accumulated impurities.

Another method is to use badger fat. It is taken orally, a teaspoon daily, and also used externally. Providing a professional massage promotes cleansing. Warming the chest and correct movements of the massage therapist will stimulate the discharge of sputum.
Restoration of the respiratory system is a long process. It will take 12-14 months. To cleanse, it is necessary not only to reduce the number of cigarettes - it is important to give them up completely. Even if you smoke 1-2, there will be no effect from the procedures performed.
Everyone saw this terrifying photo. Smoker's lungs! Recently, people have been writing online that this is part of anti-tobacco propaganda. Is it so? Let's try to figure it out.
Why do people have to breathe constantly?
Let's do an experiment: take a breath and hold your breath. You may have managed not to breathe for 20 or 30 seconds. Some people can go 23 minutes without breathing, and after a long workout, people can hold their breath for 56 minutes, but sooner or later you will be forced to take another breath because the body has no oxygen reserves (Figure 4).
Rice. 4. A person can hold their breath (Source)
A person is forced to breathe regularly to ensure that enough oxygen is supplied to our cells.
Air can enter our body through the mouth or through the nose (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Air supply(Source)
It is more useful to breathe through your nose, because it is the nose that brings the air into a state favorable to the lungs.
Anatomy and physiology
The human lungs have a lobular structure. Connective tissue septa with blood and lymphatic vessels passing through them separate areas of functional tissue from each other. The lobules are formed by the pulmonary parenchyma, a tissue that takes part in gas exchange.
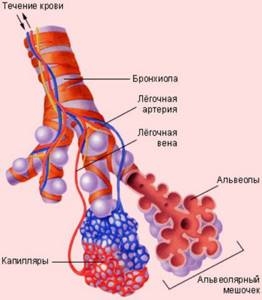
When a baby is born, its lungs are pink. As a person grows older, soot and soot, as well as tiny dust particles, are deposited in the connective tissue. Because of this, the lungs darken, the partitions between the lobules acquire clear boundaries, as if they were drawn with a black pencil.
Soot is a product of the combustion of natural or industrial hydrocarbons. It consists of tiny spherical black particles and is carried by the wind over large areas.
Belongs to the group of the most powerful carcinogens. Dangerous during pregnancy: causes mutations in the fetus. Negatively affects the growth and development of young children.
Lung damage depends on various conditions.
- living in houses with stove heating;
- work in hazardous industries (open hearth furnaces, cleaning chimneys, servicing diesel engines);
- long stays near major transport hubs and highways.
What are the consequences of inhaling tobacco smoke?
Many people do not think about what happens to the lungs when smoking. Let's try to answer this question.
Respiratory system damage
| Unlike the lungs of a non-smoker, soot accumulates not only in the connective tissue, but also in the parenchyma, damaging the delicate cells of the alveolar epithelium. |
Destroyed cells cease to participate in gas exchange.
X-ray picture
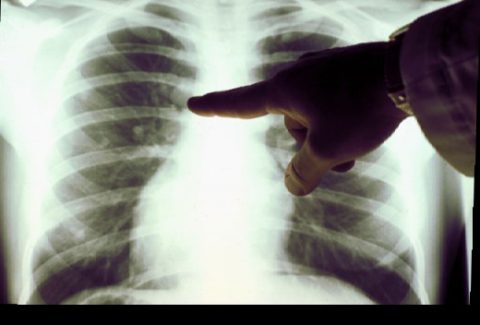
Many people are interested in: what is the difference between fluorography of a smoker’s lungs?
- "Mesh" lungs. Clearing of bronchiectasis against the background of an enhanced pulmonary pattern.
- Enlargement of the heart (deterioration of gas exchange leads to increased load on the myocardium).
- Deformation of the roots of the lungs (due to additional shadows, the shape becomes smoothed, it is difficult to differentiate its parts).
- Increased fabric density.
Diagnostics
At the initial appointment, the doctor conducts an examination (when breathing, the right or left side of the chest may be delayed), taps, and listens to the patient with a phonendoscope.
The purpose of diagnostic studies is to establish not only the fact and severity of pulmonary edema and/or hydrothorax, but also its cause.
A biochemical blood test, an analysis of the content of gases in the blood, and coagulation help to do this.
Using an X-ray, you can clearly see the accumulation of fluid, estimate its volume, detect a tumor, and damage to the lymph nodes.
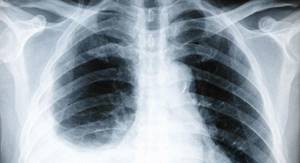
More detailed, additional information is provided by computer and magnetic resonance imaging (CT, MRI), ultrasound of the chest.
To confirm or exclude cancer, a puncture or biopsy is performed, followed by a morphological examination (cytological, histological). In the first case, fluid is taken from the pleural cavity, in the second, a fragment of pleural tissue is taken.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Is close friendship with tobacco a cause of cancer?
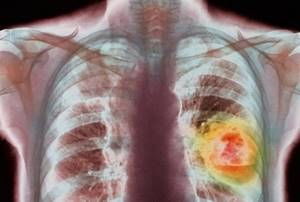
Recently, there has been an increase in cancer diseases. One of the reasons is the increase in the number of smokers, including in younger age groups.
Tobacco smoke contains more than 3,500 chemicals. Many have a carcinogenic effect: they can change the genetic information of a cell and lead to tumor transformation.
This is why lung cancer and smoking go hand in hand. Clinical studies have confirmed that 90% of patients with malignant lung tumors are tobacco lovers.

What does tobacco smoke consist of?
- hydrogen sulfide;
- carbon monoxide;
- butane;
- methanol;
- hydrocyanic acid (used by the Nazis in gas chambers);
- acetone;
- ammonia.
Tobacco smoke also contains other substances that pose a danger to human health.
Cigarette smoke contains particulate matter that settles in the lung parenchyma, causing the death of alveolar epithelial cells.
These include:
Attention! Manufacturers never indicate the full composition of cigarettes on the packaging. The sale of tobacco products brings huge profits every year. Remember that this is the price of your health.
Signs of lung cancer
Early detection of the disease gives a chance for cure and long life. Be attentive to yourself and your loved ones. Don't miss the first symptoms.
Seek help immediately if:
- worried about constant weakness;
- noticed blood in the sputum;
- the nature of the cough has changed;
- there is significant weight loss;
- shortness of breath appeared.
The photos and videos in this article will show all the dangers that await a smoker.
Remember! Annual fluorography will help detect the disease at an early stage.
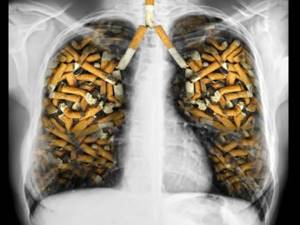
Treatment
If the cause of fluid accumulation is not cancer, drug therapy is used with diuretics (diuretics), cardiac drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, bronchodilators, expectorants and other drugs as indicated.
For malignant tumors, the use of such drugs may be symptomatic, or they are used to treat concomitant diseases. The main treatments used are chemotherapy or surgery.
- Thoracentesis – pumping out fluid from the pleural cavity. A puncture is made in the chest wall with a thin needle, after which the effusion is pumped out through a tube using an electric suction.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. It gives a quick effect, relieves the condition, but after some time the fluid accumulates again, hydrothorax resumes, and this requires repeat thoracentesis.
To avoid repeated punctures of the chest wall, a port system is installed in it, connected by a drainage tube to the pleural cavity. When fluid accumulates, the port opens and the effusion is pumped out using an electric suction device.
The intrapleural port system allows not only to pump out accumulated fluid, but also to inject drugs into the pleural cavity.
- Pleurodesis - introduction into the pleural cavity of sclerosing substances that glue the thoracic and parietal pleura. After this, the liquid has nowhere to accumulate. Pleurodesis is usually performed after draining the effusion (thoracentesis).
In case of oncological diseases, chemotherapy drugs are used for pleurodesis, which have a cytostatic effect and at the same time glue the pleural lobes together.
Along with cytostatics, the international clinic Medica24 uses immunomodulators that destroy cancer cells and show very good results of pleurodesis.
- Removal of pleura for oncological diseases in our clinic, as a rule, it is performed laparoscopically, through minimally invasive surgery.
A thoracoscope with a video camera and surgical instruments are inserted through the punctures. This allows you to avoid incisions and reduce traumatic effects.
The material was prepared by oncologist, thoraco-abdominal surgeon of the International Clinic Medica24 Alexander Valerievich Korotaev.
How to cleanse your lungs?
If you quit smoking, after a while the cough will intensify and mucous sputum will appear. This is a sign that the body has begun the cleansing process.
The release of toxins that have accumulated in the lungs for years can be lengthy. Sometimes it takes a whole year for complete cleansing.
After quitting smoking, withdrawal syndrome occurs. Neuroses and depression arise. The patient may complain of deterioration in health, increased cough. The adaptation period lasts about three months. Cleaning the lungs after smoking is possible using traditional medicine methods.

Useful tips
- Visiting the sauna or steam bath once a week. Moist warm air has a beneficial effect on the respiratory tract.
- Include pineapples in your diet. Eating these fruits daily will help cleanse your lungs and strengthen your body.
- Green tea is beneficial.
- Do breathing exercises.
Attention! The use of alternative medicine methods is not as harmless as it seems. Before use, instructions from the attending physician are required.
Herbal recipe for quick lung recovery
You need to find the following herbs:
- elder flowers;
- pine buds;
- horsetail;
- tricolor violet;
- plantain;
- lungwort;
- thyme;
- licorice.
To prepare the collection, you need to take one tablespoon of each herb.
Usage: pour 1.5 tablespoons into a glass of water, boil in a water bath for 15 minutes. Drink the decoction before bed every day for two months.
Nose is a respiratory organ
The human nose simultaneously heats the air, cleans it of impurities and most microbes, and moisturizes it. The nasal cavity is not just a channel for air, but a real labyrinth with many branches, nooks and narrow passages. This sinuous structure of the nose gives the air stream a vortex movement. Thanks to this, the inhaled air has time to warm up to 37 degrees (numerous blood vessels pass through the walls of the nose, the hot blood flowing through them quickly warms the cold air, so even on a frosty day the air enters the lungs already warmed) (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Inhaled air warms up (Source)
hairs in the nasal cavity that act as an air filter (Fig. 7).
Rice. 7. Nasal hairs trap foreign bodies (Source)
They retain dust, pollen and other harmful substances, but if foreign substances managed to bypass this barrier, they will be met by a second guard post, the mucous membrane . The upper respiratory tract is covered with a gel-like sticky liquid, mucus, which is responsible for constantly humidifying the air and protecting the lungs from foreign bodies entering them (Fig. 8). The mucous membrane has a reliable assistant, cilia .
They bend all the time (15 times per second), like grass in the wind. As soon as a foreign body hits them, they begin to push mucus with dirt stuck to it towards the throat (Fig. 9), the swallowing reflex is triggered, and the foreign body enters the stomach, where it is destroyed by hydrochloric acid, which the stomach produces (Fig. 10). Or a foreign body can be expelled during coughing or sneezing , then a sharp release of air occurs along with the foreign body (Fig. 11).
Rice. 11. Sneezing(Source)
The air stream during sneezing or coughing can reach enormous speeds from 100 km/h to 160 km/h.
Frequently asked questions to the doctor
Discomfort after smoking
Good afternoon, doctor! I've been smoking for 8 years now. I use two packs every day. I tried to quit several times, but nothing worked. Now I started to notice that my lungs hurt after smoking. What does it mean?
Hello! Your complaints are typical for chronic bronchitis. I advise you to immediately quit smoking and undergo a course of rehabilitation treatment. It is also necessary to undergo a full examination to establish a diagnosis.
Hello, Doctor! Yesterday my friend and I visited a hookah bar. Since yesterday I have been feeling heaviness in my lungs after smoking a hookah. I'm scared. What could be the consequences? Maybe I was going too deep?
Good afternoon Smoking a standard portion of hookah corresponds to several packs of cigarettes. Therefore, caution must be exercised. One visit to a hookah bar will not do much harm. After some time, your body will recover. Spend more time outdoors. Drinking plenty of fluids and breathing exercises are helpful.
Tobacco for pneumonia
Good afternoon I have focal pneumonia. I'm already recovering. Please tell me, is it possible to smoke with pneumonia - at least light cigarettes? I just die as I please.
Hello! Smoking is prohibited if you have lung diseases.
What about the Indians?
Good afternoon, doctor! You write in the article that smoking leads to lung cancer. What about the American Indians then? They smoked from early childhood until old age. Why didn’t they die out from cancer?
Hello. Firstly, during the time of Christopher Columbus there was a completely different environmental situation. It is unlikely that American Indians were exposed to carcinogens in the same way as a modern resident of a metropolis. Secondly, lung cancer occurs more often from cigarette smoking than from pipe smoking.